Nội dung bài viết
© 2026 AI VIET NAM. All rights reserved.
Tác giả: Nhóm ra đề (AIO2024)
Keywords: học deep learning online, kiểm tra năng lực deep learning, khóa học ai
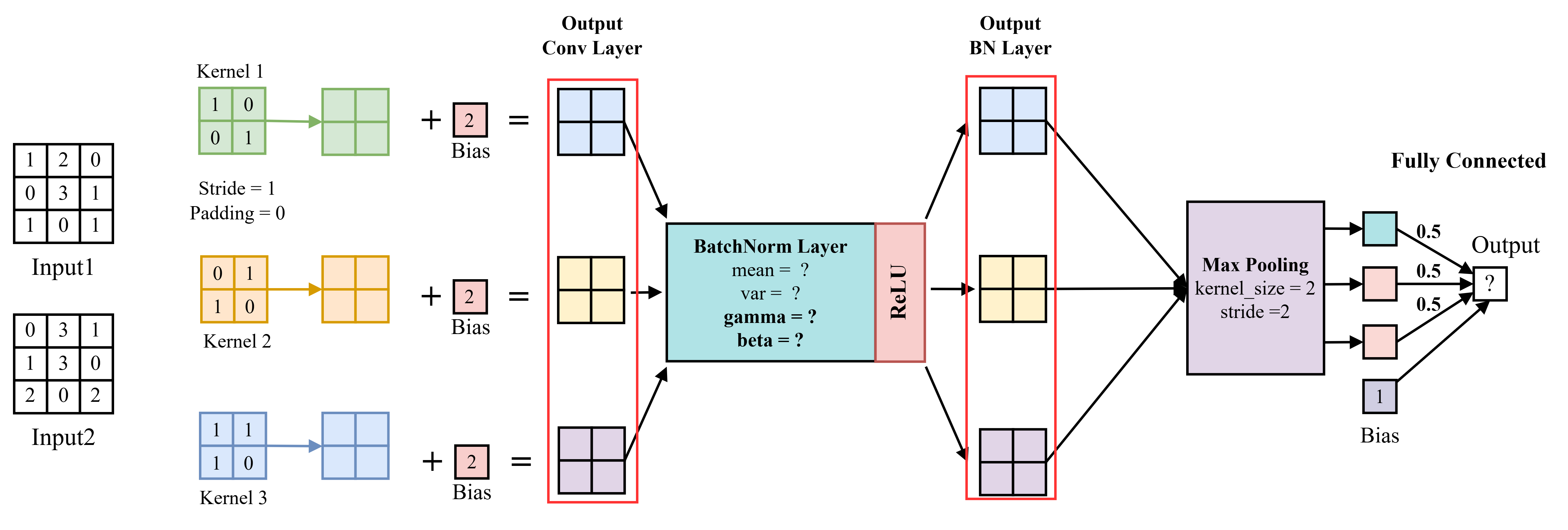
Hãy dựa vào pipeline tính toán của Convolution Model dưới đây để trả lời các câu hỏi:
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import numpy as np class CustomCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(CustomCNN, self).__init__() # Custom 2x2 convolutional layer with 3 kernels, bias=False self.conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 3, kernel_size=2, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) # Set kernel weights manually with torch.no_grad(): # Each kernel is of shape (1, 2, 2) kernel_weights = torch.tensor([ [[[1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0]]], # Kernel 1 [[[0.0, 1.0], [1.0, 0.0]]], # Kernel 2 [[[1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 0.0]]] # Kernel 3 ]) self.conv.weight.copy_(kernel_weights) # Add manual bias for after conv self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([2.0, 2.0, 2.0])) # Bias = 2 for each kernel # Initialize BatchNorm self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(3) # eps is 1e-5 # Fully connected layer self.fc = nn.Linear(3, 1, bias=True) with torch.no_grad(): self.fc.weight.fill_(0.5) self.fc.bias.fill_(1.0) def forward(self, x): # shape: (1, 1, 3, 3) x = self.conv(x) x = x + self.bias.view(1, -1, 1, 1) # manually add bias print(f"After conv:\n{x.detach().cpu().numpy().round(2)}") x = self.bn(x) print(f"After batch norm:\n{x.detach().cpu().numpy().round(2)}") print("BatchNorm stats:") print(f"Running mean: {self.bn.running_mean.data}") print(f"Running var: {self.bn.running_var.data}") print(f"Gamma (weight): {self.bn.weight.data}") print(f"Beta (bias): {self.bn.bias.data}") x = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=2, stride=2) x = x.flatten(start_dim=1) x = self.fc(x) return x
Sau khi đưa Input1 qua lớp Convolution (Conv Layer), đâu là giá trị đầu ra (feature map) đúng?
A. [[[6.0, 5.0], [2.0, 6.0]], [[4.0, 5.0], [6.0, 3.0]], [[5.0, 7.0], [6.0, 6.0]]]
B. [[[3.0, 4.0], [1.0, 5.0]], [[2.0, 2.0], [4.0, 3.0]], [[5.0, 1.0], [3.0, 2.0]]]
C. [[[7.0, 6.0], [3.0, 7.0]], [[6.0, 4.0], [5.0, 5.0]], [[7.0, 7.0], [8.0, 6.0]]]
D. [[[2.0, 3.0], [0.0, 4.0]], [[3.0, 1.0], [2.0, 0.0]], [[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 3.0]]]
Đáp án: A
input_tensor = torch.tensor( [[[ [1.0, 2.0, 0.0], [0.0, 3.0, 1.0], [1.0, 0.0, 1.0] ]], [[ [0.0, 3.0, 1.0], [1.0, 3.0, 0.0], [2.0, 0.0, 2.0] ]] ] ) model = CustomCNN() # Forward pass output = model(input_tensor) print(output)
After conv: [[[[6. 5.] [2. 6.]] [[4. 5.] [6. 3.]] [[5. 7.] [6. 6.]]] [[[5. 5.] [3. 7.]] [[6. 6.] [7. 2.]] [[6. 9.] [8. 5.]]]]
Cho một batch dữ liệu gồm hai ảnh: Input1 và Input2, được đưa qua mạng như hình minh họa ở trên. Sau khi đi qua lớp Convolution Layer, ta thu được đầu ra (feature maps) của Input2 là:
[[[5.0, 5.0], [3.0, 7.0]], [[6.0, 6.0], [7.0, 2.0]], [[6.0, 9.0], [8.0, 5.0]]]
Yêu cầu: Tính mean và variance trên toàn bộ batch data sau khi cho batch dữ liệu này qua Batch Norm Layer. Áp dụng kết quả (mean, variance) để tính toán giá trị đầu ra của Input1 sau khi qua BatchNorm Layer.
A. [[[1.12, -0.33], [0.57, 0.91]], [[-0.21, 1.35], [0.12, -0.76]], [[0.89, -1.02], [-0.45, 0.66]]]
B. [[[0.73, 0.08], [1.87, 0.73]], [[-0.54, 0.08], [0.7, -1.16]], [[-1.13, 0.38], [-0.38 -0.38]]]
C. [[[0.25, -1.44], [0.88, 0.23]], [[-1.02, 0.67], [1.12, -0.25]], [[0.43, 0.9], [-0.88, 0.11]]]
D. [[[-0.75, 1.03], [0.56, -1.01]], [[0.14, -0.63], [1.23, 0.76]], [[-0.91, 0.44], [0.35, -0.22]]]
Đáp án: B
After batch norm: [[[[ 0.73 0.08] [-1.87 0.73]] [[-0.54 0.08] [ 0.7 -1.16]] [[-1.13 0.38] [-0.38 -0.38]]] [[[ 0.08 0.08] [-1.22 1.38]] [[ 0.7 0.7 ] [ 1.32 -1.78]] [[-0.38 1.89] [ 1.13 -1.13]]]]
Để distribution của dữ liệu sau khi đi qua BN Layer có mean là 5, var là 2 thì gamma và beta có giá trị là?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: B
Với và , kết quả output cuối cùng nhận được khi đưa Input1 qua pipeline trên là?
A. 1.9034
B. 2.1078
C. 1.3453
D. 2.5120
Đáp án: A
tensor([[1.9034], [3.2944]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
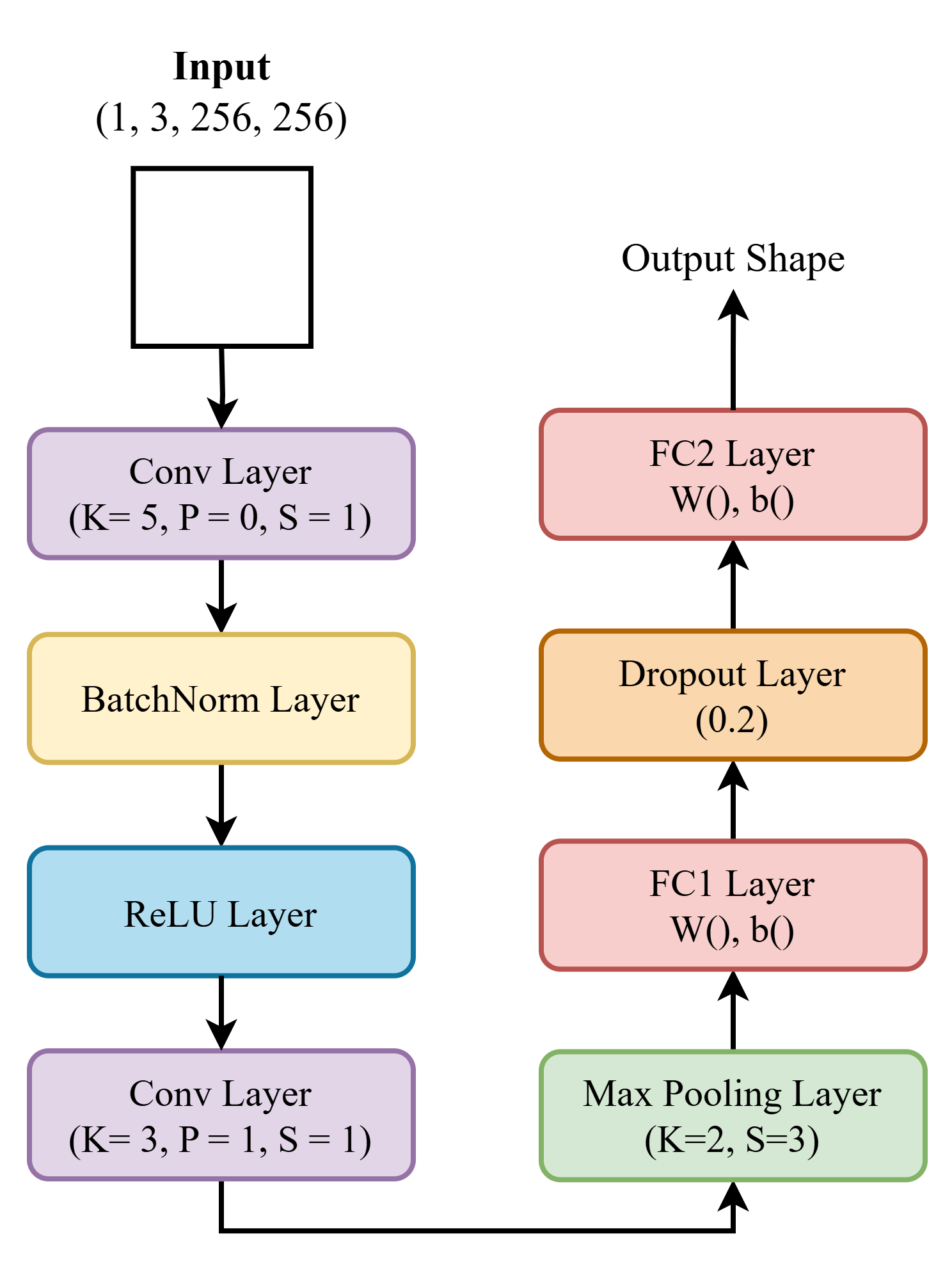
Cho pipeline tính toán convolution và input đầu vào có chứa thông tin shape và tham số cụ thể. Hãy dựa vào đó để trả lời câu hỏi liên quan tới shape dưới đây: Lưu ý: Số lượng channel được giữ nguyên 3 ở tất cả các lớp.
# Define the CNN class class CNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(CNN, self).__init__() # Conv Layer 1: K=5, P=0, S=1 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=3, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(3) # BatchNorm Layer self.relu1 = nn.ReLU() # ReLU Layer # Conv Layer 2: K=3, P=1, S=1 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # Max Pooling Layer: S=3 (assuming kernel_size=3, stride=3) self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=3) # FC1 Layer self.fc1 = nn.Linear(3 * 84 * 84, 32) # Fully connected layer print(f"FC1 Weight shape: {self.fc1.weight.shape}") print(f"FC1 Bias shape: {self.fc1.bias.shape}") self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2) # Dropout Layer (0.2) # FC2 Layer self.fc2 = nn.Linear(32, 2) # Output layer (assuming 2 classes) print(f"FC2 Weight shape: {self.fc2.weight.shape}") print(f"FC2 Bias shape: {self.fc2.bias.shape}") def forward(self, x): # Input shape print(f"Input shape: {x.shape}") # Conv1 + BatchNorm + ReLU x = self.conv1(x) print(f"After Conv1 (K=5, P=0, S=1): {x.shape}") x = self.bn1(x) print(f"After BatchNorm1: {x.shape}") x = self.relu1(x) print(f"After ReLU1: {x.shape}") # Conv2 x = self.conv2(x) print(f"After Conv2 (K=3, P=1, S=1): {x.shape}") # Max Pooling x = self.pool(x) print(f"After MaxPool (K=3, S=3): {x.shape}") # Flatten x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) print(f"After Flatten: {x.shape}") # FC1 + Dropout x = self.fc1(x) print(f"After FC1: {x.shape}") x = self.dropout(x) print(f"After Dropout (0.2): {x.shape}") # FC2 x = self.fc2(x) print(f"After FC2 (Output): {x.shape}") return x
Đưa tensor input vào pipeline, shape của tensor sau Conv1 sẽ là:
A. [1, 3, 252, 252]
B. [1, 3, 224, 224]
C. [1, 3, 219, 219]
D. [1, 3, 221, 221]
Đáp án: A
Input sau khi đi qua lớp maxpooling sẽ có shape là?
A. [1, 3, 73, 73]
B. [1, 3, 110, 110]
C. [1, 3, 74, 74]
D. [1, 3, 84, 84]
Đáp án: D
Biết PyTorch code để tạo ra FC1 là nn.Linear(x, 32), giá trị X ở đây bằng bao nhiêu?
A. 16428
B. 36300
C. 21168
D. 15987
Đáp án: C
Biết số lượng class là 2, shape của Weight trong lớp FC2 là? (không tính bias vào shape này)
A. [32, 2]
B. [2, 32]
C. [2, 16]
D. [16, 2]
Đáp án: B
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256) # Batch, Channels, Height, Width output = model(input_tensor)
Input shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256]) After Conv1 (K=5, P=0, S=1): torch.Size([1, 3, 252, 252]) After BatchNorm1: torch.Size([1, 3, 252, 252]) After ReLU1: torch.Size([1, 3, 252, 252]) After Conv2 (K=3, P=1, S=1): torch.Size([1, 3, 252, 252]) After MaxPool (K=3, S=3): torch.Size([1, 3, 84, 84]) After Flatten: torch.Size([1, 21168]) After FC1: torch.Size([1, 32]) After Dropout (0.2): torch.Size([1, 32]) After FC2 (Output): torch.Size([1, 2])
import os import copy import math import time import torch import pandas as pd import torch.nn as nn from torch.nn.functional import log_softmax, pad
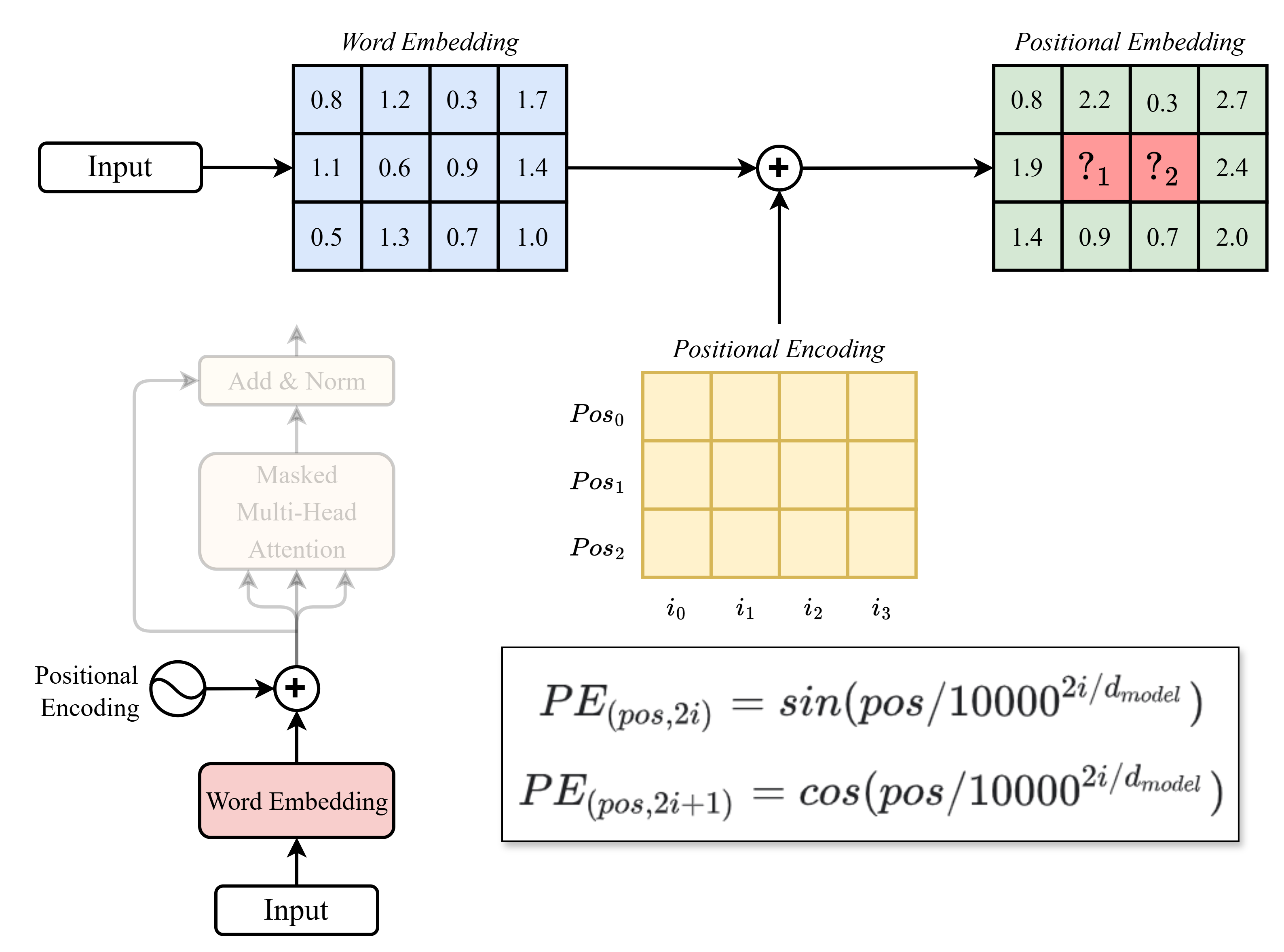
Các giá trị thiếu (các ô ký hiệu là "") trong hình lần lượt ("", "") là:
(Chỉ kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ nhất)
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: C
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module): "Implement the PE function with decorated printing" def __init__(self, d_model, max_len): super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__() print("Step 1: Initializing a zero tensor for positional encoding (pe)") pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model) print(pe) print("-" * 50) print("Step 2: Creating position indices") position = torch.arange(0, max_len).unsqueeze(1) print(position) print("-" * 50) print("Step 3: Calculating div_term (divisor term for encoding)") div_term = 1/(10000**(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2)/d_model)) print(div_term) print("-" * 50) print("Step 4: Applying sine and cosine functions to generate positional encodings") pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term) pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term) print(pe) print("-" * 50) print("Step 5: Adding a batch dimension to positional encoding") pe = pe.unsqueeze(0) self.pe = pe print(pe) print("-" * 50) def forward(self, x): result = x + self.pe[:, : x.size(1)] print("Step 6: Add Positional Encodings to the Input Embeddings", result.shape) print(result) print("-" * 50) return result d_model = 4 max_len = 3 # (Batch size = 1, max_len, d_model) input = torch.tensor([ [[0.8, 1.2, 0.3, 1.7], # <- Pos 0 [1.1, 0.6, 0.9, 1.4], # <- Pos 1 [0.5, 1.3, 0.7, 1.0]] # <- Pos 2 # i0 i1 i2 i3 ]) pos_encoding = PositionalEncoding(d_model=d_model, max_len=max_len) pos_emb = pos_encoding(input) pos_emb = torch.floor(pos_emb * 10 + 0.5) / 10 pos_emb
tensor([[[0.8000, 2.2000, 0.3000, 2.7000], [1.9000, 1.1000, 0.9000, 2.4000], [1.4000, 0.9000, 0.7000, 2.0000]]])
Các giá trị thiếu (các ô ký hiệu là "") trong hình lần lượt ("", "", "") là: (Chỉ kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ nhất)
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: D
def attention(query, key, value, mask=None): "Compute Scaled Dot Product Attention" print("Step 4.1: Extracting dimensions of query") d_k = query.size(-1) print(f"d_k (dimension of query): {d_k}") print(f"Query shape: {query.shape}") print(f"Key shape: {key.shape}") print(f"Value shape: {value.shape}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 4.2: Calculating scores -> Q.K / sqrt(d_k)") qk = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1)) print(f"QK shape (after matmul): {qk.shape}") print(f"QK:\n{qk.cpu().detach().numpy()}") scores = qk / math.sqrt(d_k) scores = torch.floor(scores * 10 + 0.5) / 10 print(f"Scores shape (after matmul): {scores.shape}") print(f"Scores (before masking):\n{scores.cpu().detach().numpy()}") print("--------------------------------------------------") if mask is not None: print("Step 4.3: Applying mask -> (Q.K / sqrt(d_k)) + Mask") scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9) print(f"Scores (after masking):\n{scores.cpu().detach().numpy()}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 4.4: Applying softmax to scores -> softmax((Q.K / sqrt(d_k)) + Mask)") p_attn = scores.softmax(dim=-1) print(f"Attention probabilities (formatted):\n{p_attn.cpu().detach().numpy()}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 4.5: Calculating output by multiplying attention probabilities with value -> softmax((Q.K / sqrt(d_k)) + Mask).V") output = torch.matmul(p_attn, value) # Attention weight Matrix * V output = torch.floor(output * 10 + 0.5) / 10 print(f"Output shape (after applying attention): {output.shape}") print(f"Output:\n{output.cpu().detach().numpy()}") print("--------------------------------------------------") return output, p_attn class MultiHeadedAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, h, d_model): "Take in model size and number of heads" super(MultiHeadedAttention, self).__init__() print("Step 1: Initializing dimensions and layers") self.d_k = d_model // h self.d_v = d_model // h self.h = h self.attn = None print(f"d_k (dimension per head): {self.d_k}") print(f"d_v (dimension per head): {self.d_v}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 2: Initializing Linear layers for Q, K, V") self.W_Q = nn.Linear(d_model, self.d_k) self.W_K = nn.Linear(d_model, self.d_k) self.W_V = nn.Linear(d_model, self.d_v) print(f"W_Q weights initialized: {self.W_Q.weight.shape}") print(f"W_K weights initialized: {self.W_K.weight.shape}") print(f"W_V weights initialized: {self.W_V.weight.shape}") print("--------------------------------------------------") # Set custom weights and biases for W_Q, W_K, W_V with torch.no_grad(): print("Step 3: Setting custom weights and biases") # W_Q self.W_Q.weight.copy_(torch.tensor([ [0.5, 0.3, 0.7, 0.2], [0.8, 0.1, 0.5, 0.2], [0.3, 0.8, 0.9, 0.5], [0.5, 0.8, 0.9, 0.2] ])) # self.W_Q.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.2, 0.4])) self.W_Q.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0.2, 0.7, 0.8, 0.8])) print(f"W_Q weights: \n{self.W_Q.weight.cpu().numpy()}\n") print(f"W_Q bias: \n{self.W_Q.bias.cpu().numpy()}\n") # W_K self.W_K.weight.copy_(torch.tensor([ [0.2, 0.7, 0.2, 0.5], [0.8, 0.8, 0.2, 0.8], [0.5, 0.3, 0.8, 0.8], [0.2, 0.9, 0.2, 0.7] ])) # self.W_K.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0.8, 0.6, 0.4, 0.2])) self.W_K.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0.5, 0.5, 0.8, 0.2])) print(f"W_K weights: \n{self.W_K.weight.cpu().numpy()}\n") print(f"W_K bias: \n{self.W_K.bias.cpu().numpy()}\n") # W_V self.W_V.weight.copy_(torch.tensor([ [0.07, 0.33, 0.03, 0.37], [0.12, 0.28, 0.18, 0.22], [0.27, 0.13, 0.23, 0.17], [0.38, 0.04, 0.32, 0.06] ])) self.W_V.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0.28, 0.47, 0.72, 0.95])) print(f"W_V weights: \n{self.W_V.weight.cpu().numpy()}\n") print(f"W_V bias: \n{self.W_V.bias.cpu().numpy()}\n") print("--------------------------------------------------") def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None): if mask is not None: print("Step 1: Adding mask for all heads") mask = mask.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.h, -1, -1) print(f"Mask shape after expansion: {mask.shape}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 2: Input shapes") print(f"Query input shape: {query.shape}") print(f"Key input shape: {key.shape}") print(f"Value input shape: {value.shape}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 3: Applying Linear layers to compute Q, K, V") Q = self.W_Q(query).view(query.size(0), -1, self.h, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2) Q = torch.floor(Q * 10 + 0.5) / 10 K = self.W_K(key).view(key.size(0), -1, self.h, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2) K = torch.floor(K * 10 + 0.5) / 10 V = self.W_V(value).view(value.size(0), -1, self.h, self.d_v).transpose(1, 2) V = torch.floor(V * 10 + 0.5) / 10 print(f"Q (Query) shape after Linear and reshape: {Q.shape}") print(f"Q (Query):\n{Q.cpu().detach().numpy()}\n") print(f"K (Key) shape after Linear and reshape: {K.shape}") print(f"K (Key):\n{K.cpu().detach().numpy()}\n") print(f"V (Value) shape after Linear and reshape: {V.shape}") print(f"V (Value):\n{V.cpu().detach().numpy()}\n") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 4: Computing attention") x, self.attn = attention(Q, K, V, mask=mask) x = x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(query.size(0), -1, self.h * self.d_v) print(f"Final output shape: {x.shape}") print(x) return x
query = pos_emb key = pos_emb value = pos_emb mask = torch.tensor([[[1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]]]) heads = 1 multi_head_attention = MultiHeadedAttention(heads, d_model) attention_output = multi_head_attention(query, key, value, mask)
Q (Query) shape after Linear and reshape: torch.Size([1, 1, 3, 4]) Q (Query): [[[[2. 2.3 4.4 3.8] [2.6 3.3 4.3 3.9] [2.1 2.7 3.6 3.2]]]] K (Key) shape after Linear and reshape: torch.Size([1, 1, 3, 4]) K (Key): [[[[3.6 5.1 4.3 4.3] [3. 5. 4.7 3.4] [2.6 4.1 3.9 2.8]]]] V (Value) shape after Linear and reshape: torch.Size([1, 1, 3, 4]) V (Value): [[[[2.1 1.8 1.8 1.6] [1.7 1.7 2. 2.1] [1.4 1.5 1.7 1.9]]]]
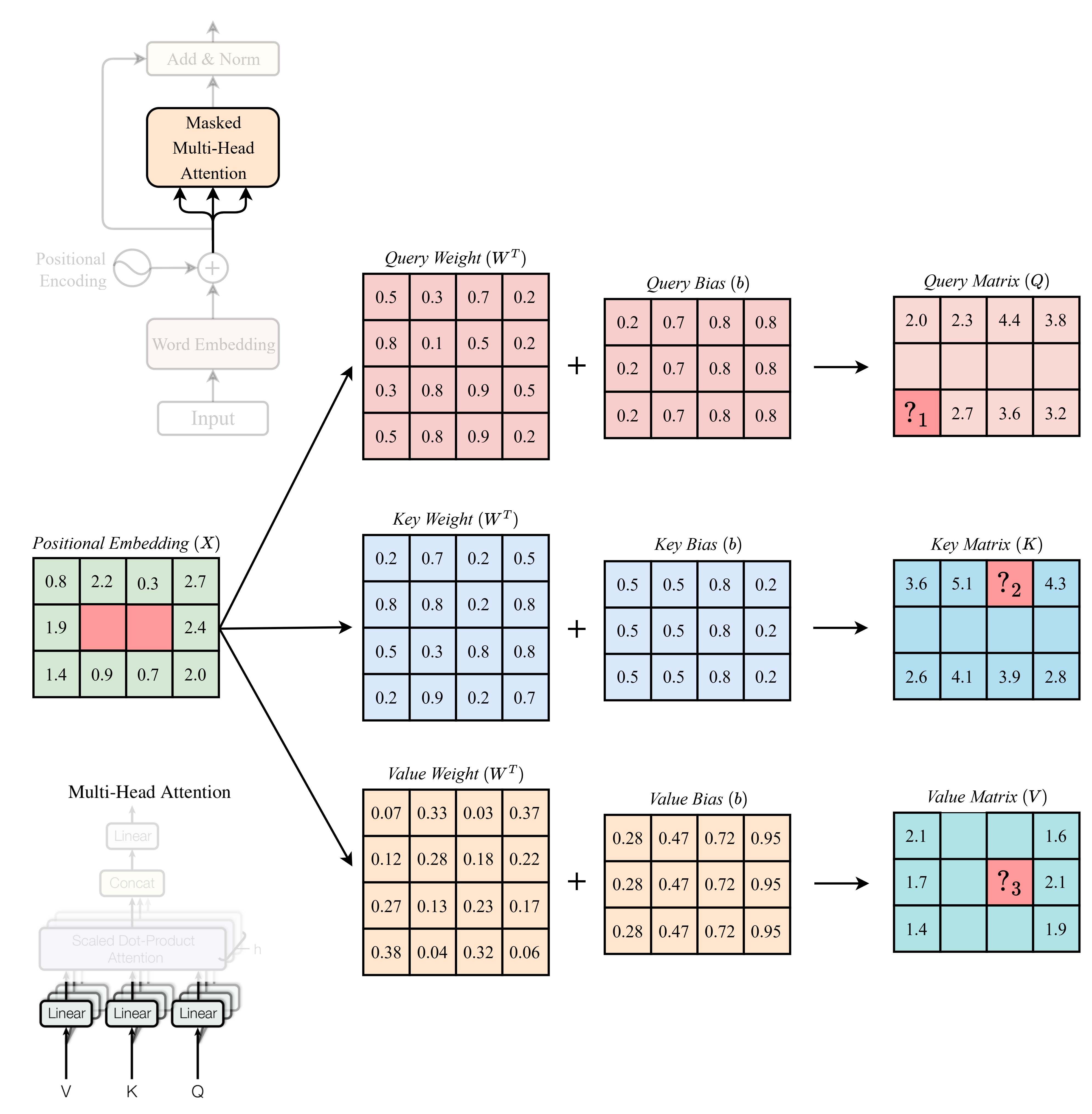
Sử dụng kết quả từ câu trước, tính các giá trị thiếu (các giá trị "") trong hình lần lượt ("", "") là: (Chỉ kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ nhất)
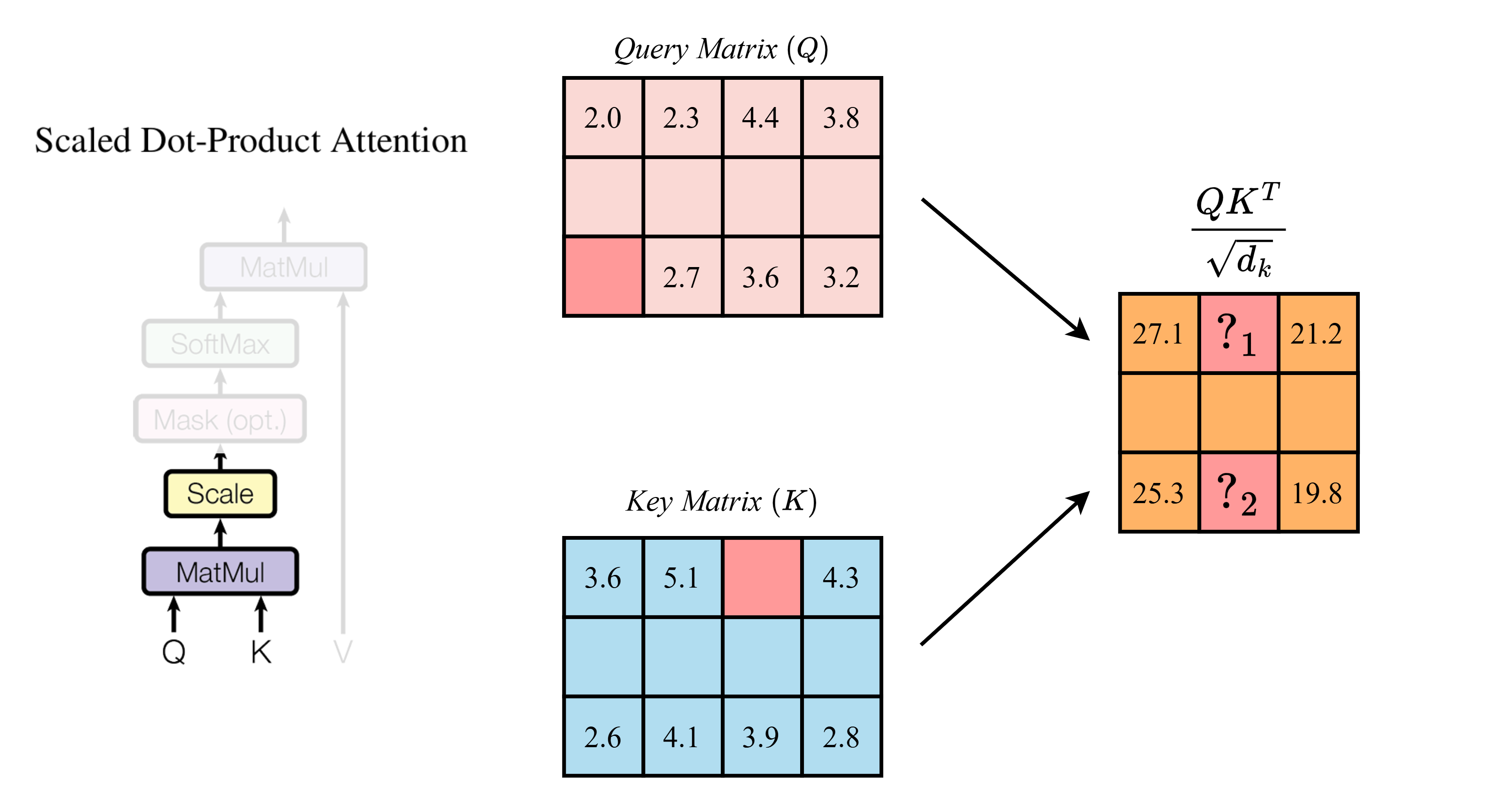
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: B
Scores (before masking): [[[[27.1 25.6 21.2] [30.7 28.9 24. ] [25.3 23.8 19.8]]]]
Sử dụng kết quả từ câu trước, tính các giá trị thiếu (các giá trị "") trong hình lần lượt ("", "") là: (Chỉ kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ nhất)
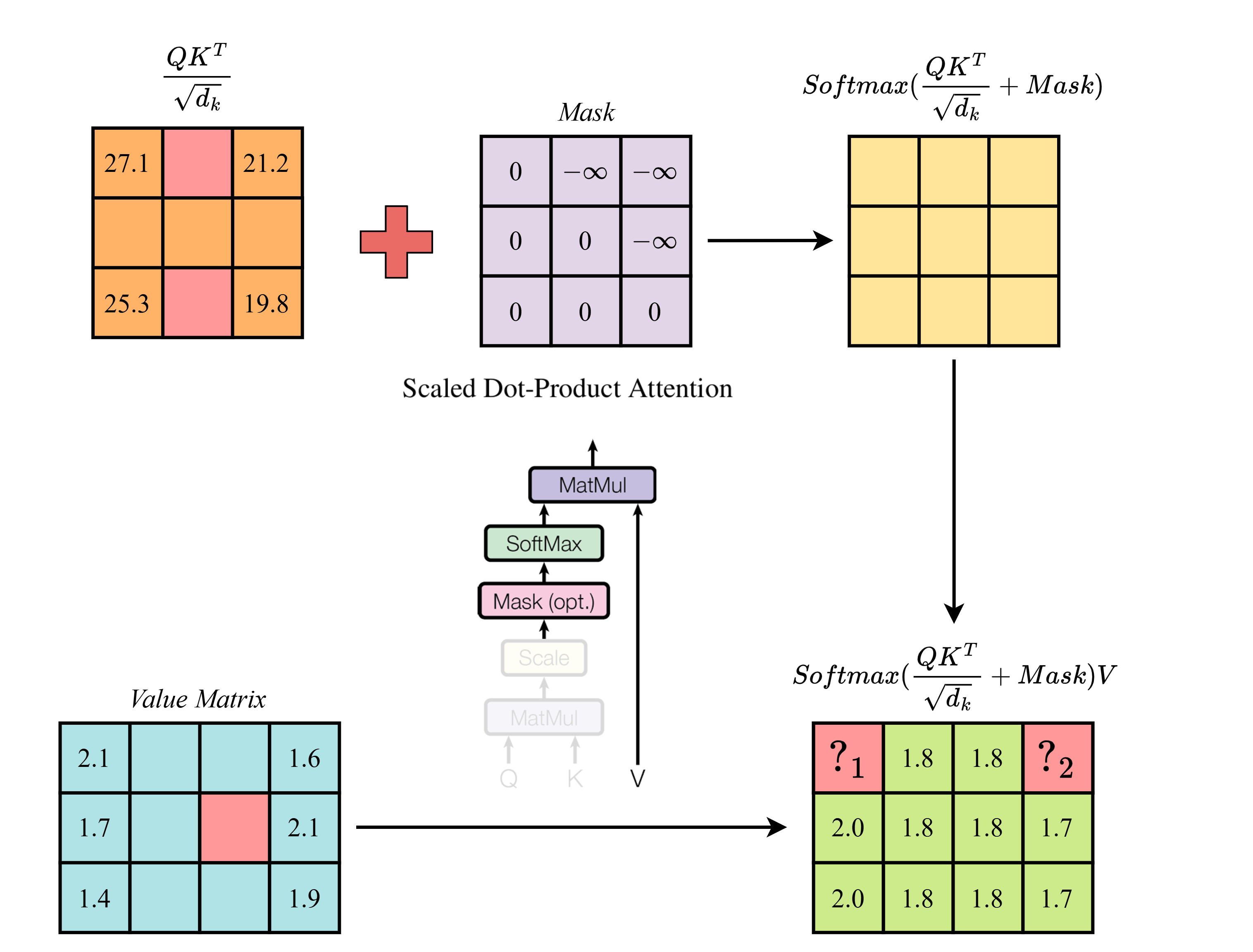
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: A
Step 4.5: Calculating output by multiplying attention probabilities with value -> softmax((Q.K / sqrt(d_k)) + Mask).V Output shape (after applying attention): torch.Size([1, 1, 3, 4]) Output: [[[[2.1 1.8 1.8 1.6] [2. 1.8 1.8 1.7] [2. 1.8 1.8 1.7]]]]
Sử dụng kết quả từ câu trước, tính các giá trị thiếu (các giá trị "") trong hình lần lượt ("", "") là: (Chỉ kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ hai)
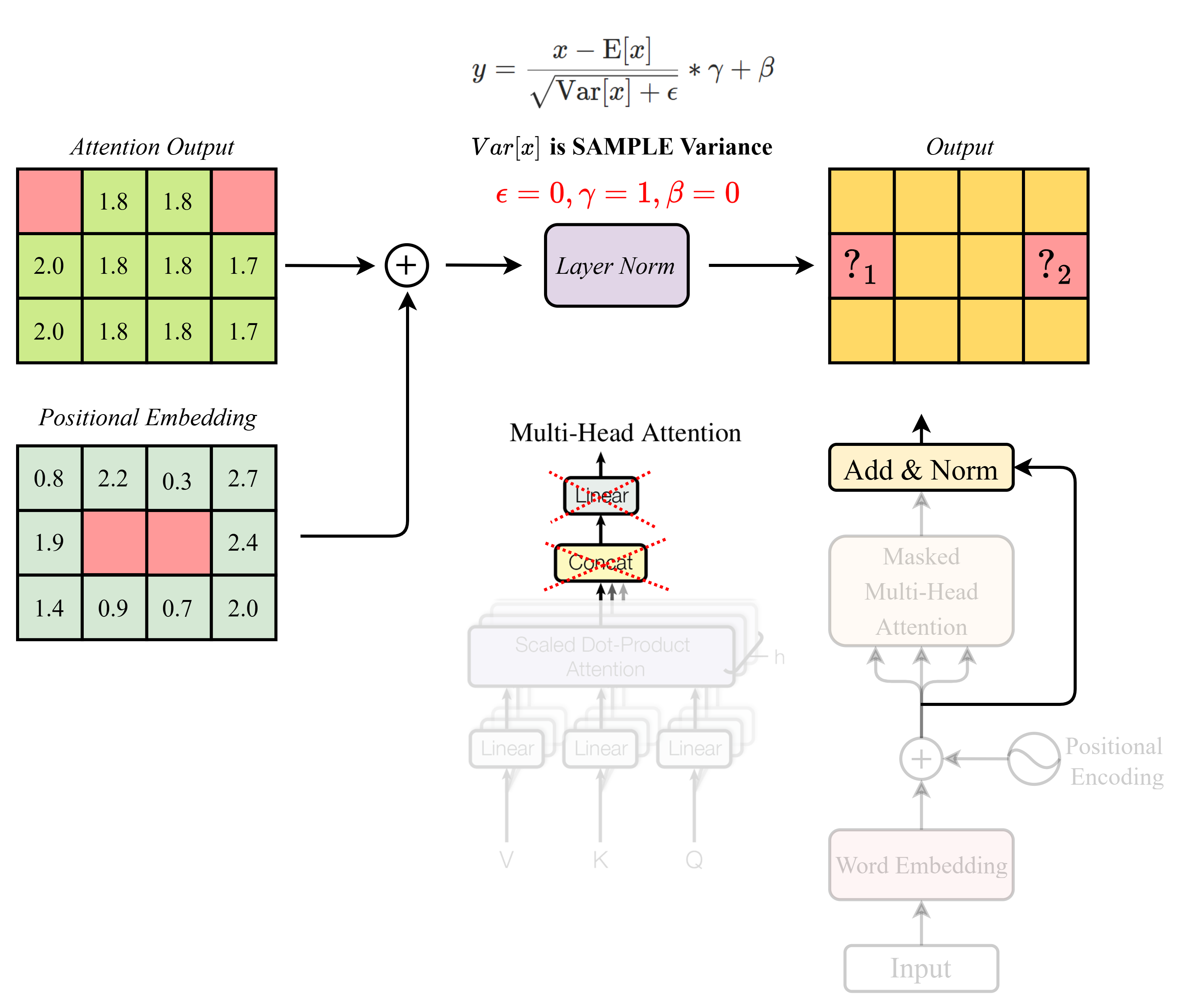
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: C
class LayerNorm(nn.Module): "Construct a layernorm module" def __init__(self, features, eps=0): super(LayerNorm, self).__init__() self.a_2 = torch.ones(features) self.b_2 = torch.zeros(features) self.eps = eps def forward(self, x): print("Step 2.1: Calculating mean and standard deviation") mean = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True) std = x.std(-1, keepdim=True) print(f"Mean shape: {mean.shape}, Values: {mean.flatten().tolist()}") print(f"Standard deviation shape: {std.shape}, Values: {std.flatten().tolist()}") print("--------------------------------------------------") print("Step 2.2: Normalizing the input") normalized_x = self.a_2 * (x - mean) / (std + self.eps) + self.b_2 print(f"Normalized output shape: {normalized_x.shape}") print("--------------------------------------------------") return normalized_x class AddNorm(nn.Module): def __init__(self, size): super(AddNorm, self).__init__() self.norm = LayerNorm(size) def forward(self, x, res_x): print("Step 1: Adding residual connection") add_x = x + res_x print(f"After Adding shape: {add_x.shape}") print(add_x.detach().cpu().numpy()) print("--------------------------------------------------\n") print("Step 2: Applying LayerNorm") norm_x = self.norm(add_x) # norm_x = torch.floor(norm_x * 100 + 0.5) / 100 print(f"Final output shape: {norm_x.shape}") print(norm_x) print("--------------------------------------------------") return norm_x addnorm = AddNorm(d_model) add_norm = addnorm(attention_output, pos_emb)
Final output shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 4]) tensor([[[-0.4189, 0.6654, -1.2075, 0.9611], [ 0.7119, -0.7119, -0.9966, 0.9966], [ 0.5723, -0.6603, -1.0125, 1.1006]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
Mô tả:
Giả sử ta có một mạng RNN đơn giản với input size = 3 và hidden size = 2. Trọng số của mạng chi tiết như hình bên dưới.
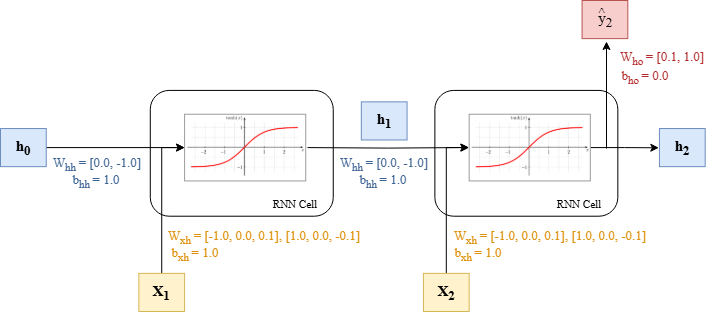
import torch import numpy as np import torch.nn as nn class RNNCell(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, bias=True, nonlinearity="tanh"): super(RNNCell, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.bias = bias if nonlinearity not in ["tanh", "relu"]: raise ValueError("Invalid nonlinearity. Choose 'tanh' or 'relu'.") self.nonlinearity = nonlinearity # Linear transformations self.input_to_hidden = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.hidden_to_hidden = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) def set_weights(self, input_to_hidden_weight, hidden_to_hidden_weight, input_to_hidden_bias, hidden_to_hidden_bias): self.input_to_hidden.weight.data = input_to_hidden_weight self.hidden_to_hidden.weight.data = hidden_to_hidden_weight self.input_to_hidden.bias.data = input_to_hidden_bias self.hidden_to_hidden.bias.data = hidden_to_hidden_bias def forward(self, input, hidden_state_input=None): if hidden_state_input is None: hidden_state_input = input.new_zeros(input.size(0), self.hidden_size, requires_grad=False) # Compute the new hidden state hidden_state = self.input_to_hidden(input) + self.hidden_to_hidden(hidden_state_input) hidden_state = torch.tanh(hidden_state) if self.nonlinearity == "tanh" else torch.relu(hidden_state) return hidden_state
Đầu vào của mạng tại timestep 1 và timestep 2 lần lượt là , có input size = 3 và cho biết:
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính toán hidden state tại timestep 2 .
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: A
# 1. Tính output của lớp hidden layer (có bias), với d_h = 2. X = torch.tensor([ [1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0], ]) torch.manual_seed(42) rnn = RNNCell(input_size=3, hidden_size=2) input_to_hidden_weight = torch.tensor([[-1.0, 0.0, 0.1], [1.0, 0.0, -0.1]]) input_to_hidden_bias = torch.tensor([1.0]) hidden_to_hidden_weight = torch.tensor([[0.0, -1.0]]) hidden_to_hidden_bias = torch.tensor([1.0]) rnn.set_weights(input_to_hidden_weight, hidden_to_hidden_weight, input_to_hidden_bias, hidden_to_hidden_bias) with torch.no_grad(): # Output of the hidden state hidden_state = None for i in range(2): hidden_state = rnn(X[i].unsqueeze(0), hidden_state) print("Output of the hidden state at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, hidden_state)) print(f"\nĐáp án: A. {hidden_state}")
Output of the hidden state at time step 0: tensor([[0.8617, 0.9910]]) Output of the hidden state at time step 1: tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]]) Đáp án: A. tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]])
Tiếp tục với mạng RNN ở câu FNE2RNN01, ta thêm một lớp fully connected với output size = 1 để thực hiện bài toán regression. Trọng số của lớp fully connected và được khởi tạo như hình trên.
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính toán output của mạng RNN sau khi đi qua lớp fully connected.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: B
# 2. Tính output của model ở lớp cuối cùng, với d_out = 1. (regression). hidden_state = torch.tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]]) print("Final hidden state: \n{}".format(hidden_state)) hidden_to_output = nn.Linear(2, 1, bias=True) hidden_to_output.weight.data = torch.tensor([[0.1, 1.0]]) hidden_to_output.bias.data = torch.tensor([0.0]) with torch.no_grad(): output = hidden_to_output(hidden_state) print("Output: {}".format(output)) print(f"\n\nĐáp án: B. {output}")
Final hidden state: tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]]) Output: tensor([[0.9014]]) Đáp án: B. tensor([[0.9014]])
Mô tả:
Giả sử ta muốn dùng mạng RNN ở câu FNE2RNN01 để thực hiện bài toán sequence labeling. Ta thêm vào mỗi timestep một lớp Fully Connected để chuyển đổi giá trị hidden state thành giá trị dự đoán output . Mỗi giá trị dự đoán tại mỗi timestep có output size = 2, tương ứng với xác suất mà mô hình dự đoán timestep đó thuộc vào lớp 0 hoặc lớp 1. Trọng số của các lớp được khởi tạo chi tiết như trong hình bên dưới.
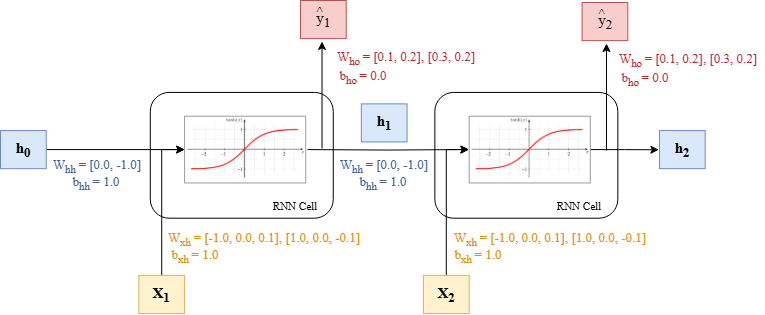
Câu hỏi:
Tính xem và lần lượt được mạng RNN dự đoán có nhãn là gì?
A. 0, 0
B. 0, 1
C. 1, 0
D. 1, 1
Đáp án: C
# 3. Chuyển bài toán thành bài toán Sequence Labeling, tính output của từng time-steps. # Giả sử mỗi hàng là một embedding của một từ trong câu, và mỗi từ được gán nhãn 0 hoặc 1. hidden_to_output = nn.Linear(2, 2, bias=True) hidden_to_output.weight.data = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2], [0.3, 0.2]]) hidden_to_output.bias.data = torch.tensor([0.0]) hidden_state = None with torch.no_grad(): for i in range(2): print() print(25 * "*") hidden_state = rnn(X[i].unsqueeze(0), hidden_state) print("Output of the hidden state at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, hidden_state)) output = nn.Softmax(dim=1)(hidden_to_output(hidden_state)) print("Output at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, output)) print("\nPredicted label at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, torch.argmax(output, dim=1))) print(f"\n\nĐáp án: C. 1, 0")
************************* Output of the hidden state at time step 0: tensor([[0.8617, 0.9910]]) Output at time step 0: tensor([[0.4570, 0.5430]]) Predicted label at time step 0: tensor([1]) ************************* Output of the hidden state at time step 1: tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]]) Output at time step 1: tensor([[0.5490, 0.4510]]) Predicted label at time step 1: tensor([0]) Đáp án: C. 1, 0
Mô tả
Ta có một mạng Bidirectional RNN với input size = 3 và hidden size = 2. Trọng số của mạng được khởi tạo giống như hình bên dưới.
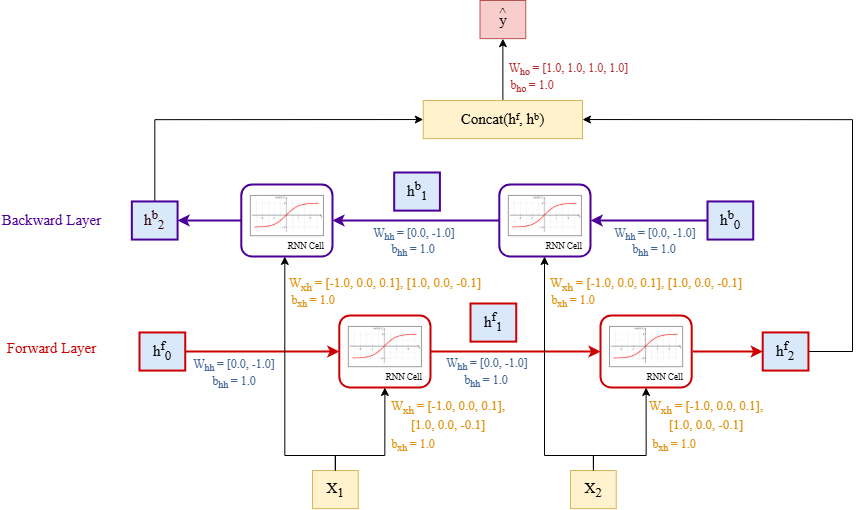
Đầu vào của mạng tại timestep 1 và timestep 2 lần lượt là , có input size = 3 và cho biết:
Câu hỏi:
Tính giá trị output cuối cùng của mạng (không sử dụng softmax).
A. 2.2681
B. 2.2431
C. 2.2181
D. 2.1931
Đáp án: B
# 4. Bidirectional RNN, đưa ra output cuối cùng. # Giá trị trọng số 2 mạng là như nhau, tính output của model ở lớp cuối cùng. forward_rnn = RNNCell(input_size=3, hidden_size=2) backward_rnn = RNNCell(input_size=3, hidden_size=2) forward_rnn.set_weights(input_to_hidden_weight, hidden_to_hidden_weight, input_to_hidden_bias, hidden_to_hidden_bias) backward_rnn.set_weights(input_to_hidden_weight, hidden_to_hidden_weight, input_to_hidden_bias, hidden_to_hidden_bias) hidden_to_output = nn.Linear(4, 1, bias=True) hidden_to_output.weight.data = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]]) hidden_to_output.bias.data = torch.tensor([1.0]) hidden_state_forward = None hidden_state_backward = None with torch.no_grad(): for i in range(2): print() print(25 * "*") hidden_state_forward = forward_rnn(X[i].unsqueeze(0), hidden_state_forward) hidden_state_backward = backward_rnn(X[1-i].unsqueeze(0), hidden_state_backward) print("Output - hidden state Forward at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, hidden_state_forward)) print("Output - hidden state Backward at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, hidden_state_backward)) if i == 1: hidden_state = torch.cat((hidden_state_forward, hidden_state_backward), dim=1) output = hidden_to_output(hidden_state) print("\nOutput at time step {}: \n{}".format(i, output)) print(f"\n\nĐáp án: B. {output}")
************************* Output - hidden state Forward at time step 0: tensor([[0.8617, 0.9910]]) Output - hidden state Backward at time step 0: tensor([[-0.8854, 1.0000]]) ************************* Output - hidden state Forward at time step 1: tensor([[-0.9834, 0.9997]]) Output - hidden state Backward at time step 1: tensor([[0.2913, 0.9354]]) Output at time step 1: tensor([[2.2431]]) Đáp án: B. tensor([[2.2431]])
Mô tả:
Ta có một mạng LSTM đơn giản như hình bên dưới với input size = 3 và hidden size = 2.
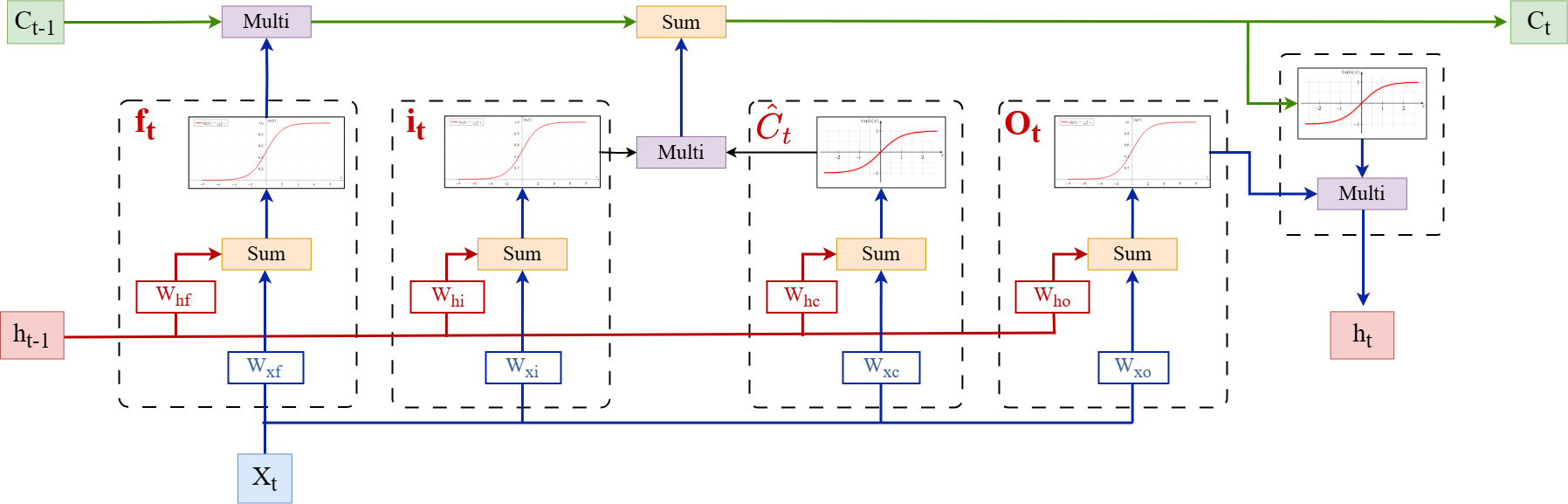
Lưu ý rằng mô hình không có bias để đơn giản hóa tính toán.
Trọng số của mạng được khởi tạo như sau:
,
,
,
,
Đầu vào của mạng tại timestep t là và cho biết:
import torch import numpy as np import torch.nn as nn class LSTMCell(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, bias=False): super(LSTMCell, self).__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.bias = bias # Linear layers for input-to-hidden and hidden-to-hidden transformations self.hidden_to_forget = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.hidden_to_input = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.hidden_to_cell = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.hidden_to_output = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.input_to_forget = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.input_to_input = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.input_to_cell = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) self.input_to_output = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias) def set_weights(self, input_to_forget_weight, input_to_input_weight, input_to_cell_weight, input_to_output_weight, hidden_to_forget_weight, hidden_to_input_weight, hidden_to_cell_weight, hidden_to_output_weight): self.input_to_forget.weight.data = input_to_forget_weight self.input_to_input.weight.data = input_to_input_weight self.input_to_cell.weight.data = input_to_cell_weight self.input_to_output.weight.data = input_to_output_weight self.hidden_to_forget.weight.data = hidden_to_forget_weight self.hidden_to_input.weight.data = hidden_to_input_weight self.hidden_to_cell.weight.data = hidden_to_cell_weight self.hidden_to_output.weight.data = hidden_to_output_weight def forward(self, input, hidden_state_tuple=None): # If hidden state is not provided, initialize it to zeros (the first time step) if hidden_state_tuple is None: hidden_state_tuple = input.new_zeros(input.size(0), self.hidden_size, requires_grad=False) hidden_state_tuple = (hidden_state_tuple, hidden_state_tuple) hidden_state, cell_state_prev = hidden_state_tuple # Compute gates input_gate = self.input_to_input(input) + self.hidden_to_input(hidden_state) # Add gate forget_gate = self.input_to_forget(input) + self.hidden_to_forget(hidden_state) # Forget gate cell_gate = self.input_to_cell(input) + self.hidden_to_cell(hidden_state) output_gate = self.input_to_output(input) + self.hidden_to_output(hidden_state) # Output gate # Apply nonlinearities i_t = torch.sigmoid(input_gate) f_t = torch.sigmoid(forget_gate) g_t = torch.tanh(cell_gate) o_t = torch.sigmoid(output_gate) print("\n\nCâu 1:") print("Input gate: \n{}".format(i_t)) print("\n\nCâu 2:") print("Output gate: \n{}".format(o_t)) # Update cell state and hidden state cell_state_next = f_t * cell_state_prev + i_t * g_t hidden_state_next = o_t * torch.tanh(cell_state_next) return hidden_state_next, cell_state_next
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính output của input gate.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: D
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính output của output gate.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: B
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính giá trị của .
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: A
Câu hỏi:
Hãy tính giá trị của .
A.
B.
C.
D.
Đáp án: A
X = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0]]) lstm = LSTMCell(input_size=3, hidden_size=2) classification = nn.Linear(2, 1, bias=True) input_to_forget_weight = torch.tensor([[1.0, 0.0, 0.1], [1.0, 0.0, -0.1]]) input_to_input_weight = torch.tensor([[-1.0, 0.0, 0.2], [-1.0, 0.0, -0.2]]) input_to_cell_weight = torch.tensor([[1.0, 0.0, -0.3], [1.0, 0.0, -0.3]]) input_to_output_weight = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 0.4], [1.0, -1.0, -0.4]]) hidden_to_forget_weight = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [0.0, -1.0]]) hidden_to_input_weight = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [0.0, -1.0]]) hidden_to_cell_weight = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [0.0, -1.0]]) hidden_to_output_weight = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [0.0, -1.0]]) lstm.set_weights(input_to_forget_weight, input_to_input_weight, input_to_cell_weight, input_to_output_weight, hidden_to_forget_weight, hidden_to_input_weight, hidden_to_cell_weight, hidden_to_output_weight) hidden_state_tuple = None with torch.no_grad(): hidden_state_tuple, cell_state_tuple = lstm(X[0].unsqueeze(0), hidden_state_tuple) print("\n\nCâu 3:") print("Cell state at timestep t: \n{}".format(cell_state_tuple[0])) print("\n\nCâu 4:") print("Hidden state at timestep t: \n{}".format(hidden_state_tuple[0]))
Câu 1: Input gate: tensor([[0.4013, 0.1680]]) Câu 2: Output gate: tensor([[0.9852, 0.0998]]) Câu 3: Cell state at timestep t: tensor([0.0400, 0.0167]) Câu 4: Hidden state at timestep t: tensor([0.0394, 0.0017])
Bài viết liên quan
Bài thi cuối khóa AIO2024 - Phần 1 (Machine Learning)
tháng 6 2025
Phần 1 trong bốn phần thi cuối khóa AIO2024. Phần này kiểm tra kiến thức machine learning với các kỹ năng và kiến thức về toán và lập trình Python.
