Nội dung bài viết
© 2026 AI VIET NAM. All rights reserved.
Tác giả: Nhóm ra đề (2024)
Keywords: học deep learning online, kiểm tra năng lực deep learning, khóa học ai
Cho trước hàm loss của YOLOv1.
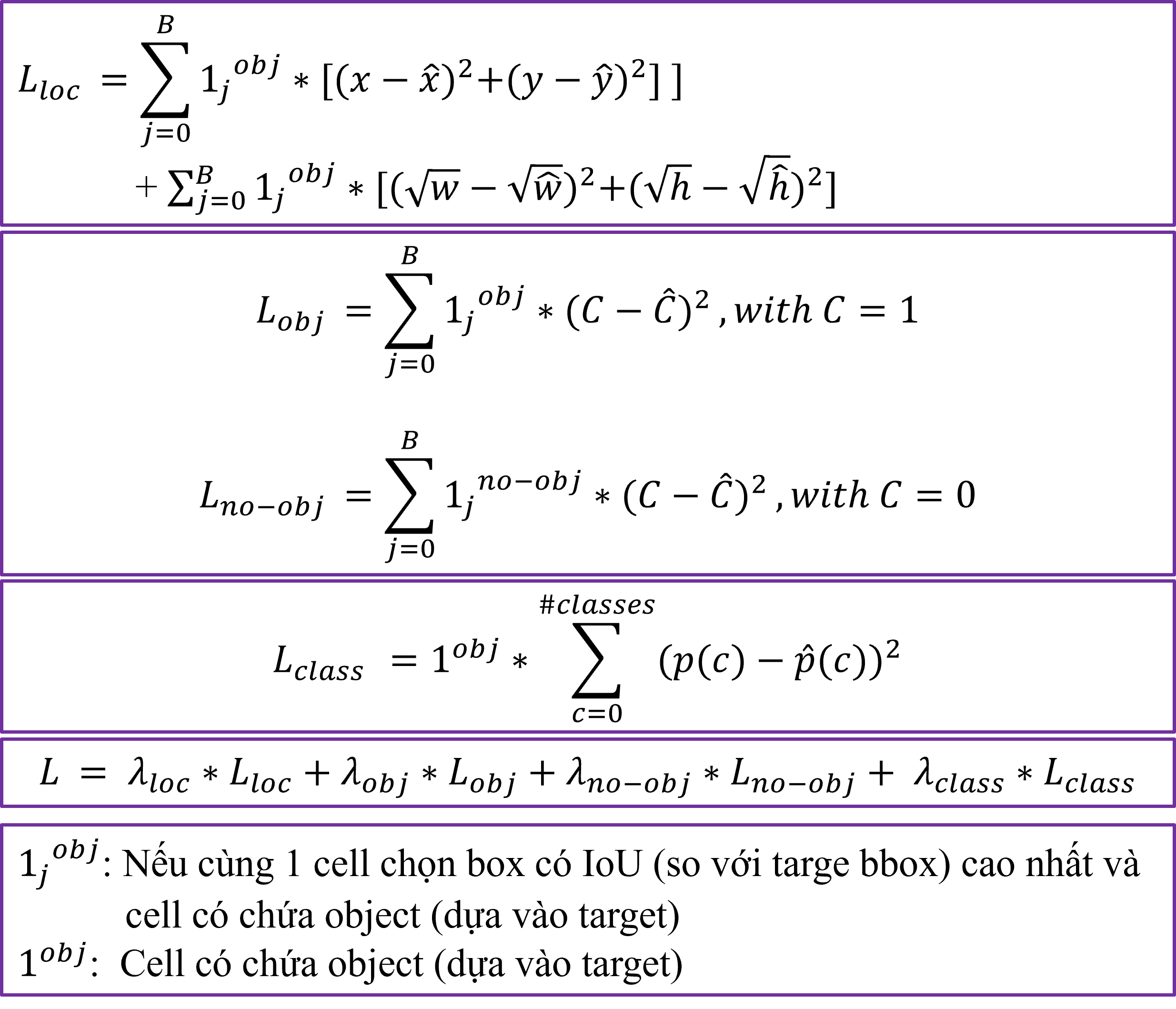

Giả thiết bài toán:

Hãy xác định output shape của mô hình là bao nhiêu?
A. (N, 25)
B. (N, 15)
C. (N, 35)
D. (N, 45)
Kết luận: Shape của vector đầu ra là (N, 35), trong đó N là số lượng ảnh trong một batch.
Đáp án: C
Cho trước hàm loss của YOLOv1.

Giả thiết bài toán:

Hãy xác định output shape của mô hình là bao nhiêu?
A. (N, 30)
B. (N, 32)
C. (N, 35)
D. (N, 40)
Kết luận: Shape của vector đầu ra là (N, 32).
Đáp án: B
Cho trước hàm loss của YOLOv1.

Giả thiết bài toán:

Hãy xác định output shape của mô hình là bao nhiêu?
A. (N, 29)
B. (N, 30)
C. (N, 32)
D. (N, 35)
Kết luận: Shape của vector đầu ra là (N, 29).
Đáp án: A
Cho trước hàm loss của YOLOv1.

Giả thiết bài toán:

Hãy xác định output shape của mô hình là bao nhiêu?
A. (N, 20)
B. (N, 26)
C. (N, 29)
D. (N, 35)
Kết luận: Shape của vector đầu ra là (N, 26).
Đáp án: B
YOLOv3 và YOLOv5 dùng thêm kỹ thuật multi-scale detection sẽ giúp cải thiện độ chính xác cho ảnh nào sau đây:
A. 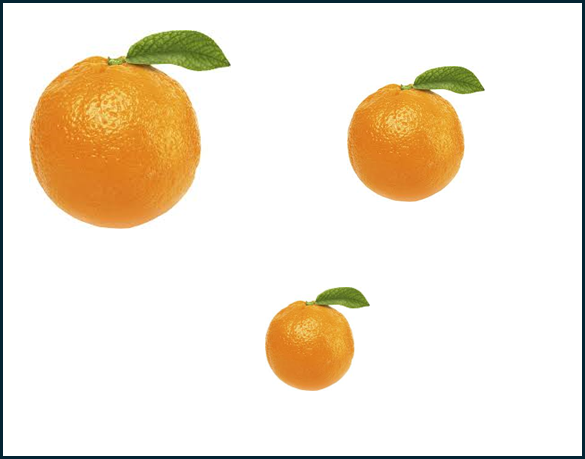
B. 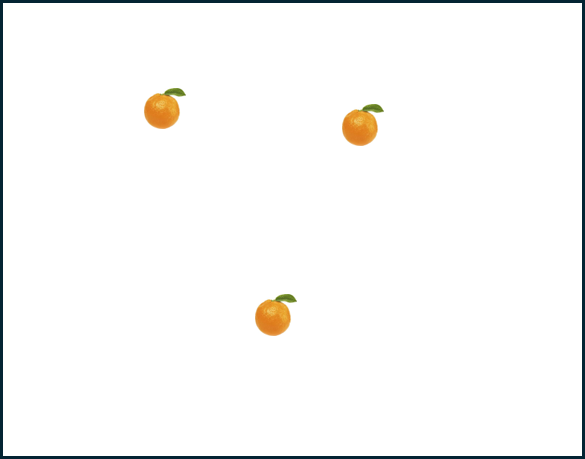
C. 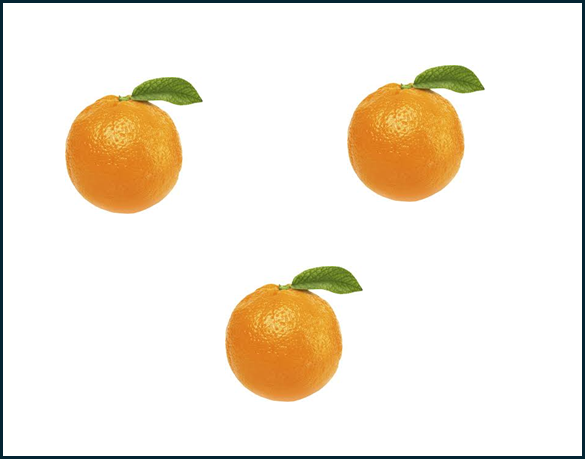
D.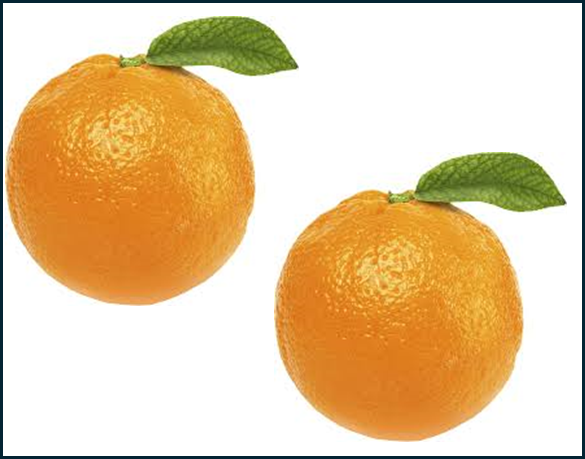 
Giải thích: Kỹ thuật multi-scale detection trong YOLOv3 và YOLOv5 cho phép mô hình phát hiện các đối tượng ở nhiều kích thước khác nhau, từ nhỏ đến lớn. Điều này rất quan trọng trong các bức ảnh có đối tượng có kích thước khác nhau, như trong trường hợp của bức ảnh A, nơi có quả cam nhỏ, vừa và lớn. Các bức ảnh B, C và D có đối tượng có kích thước tương đối đồng nhất, do đó không cần thiết phải sử dụng multi-scale detection.
Đáp án: A
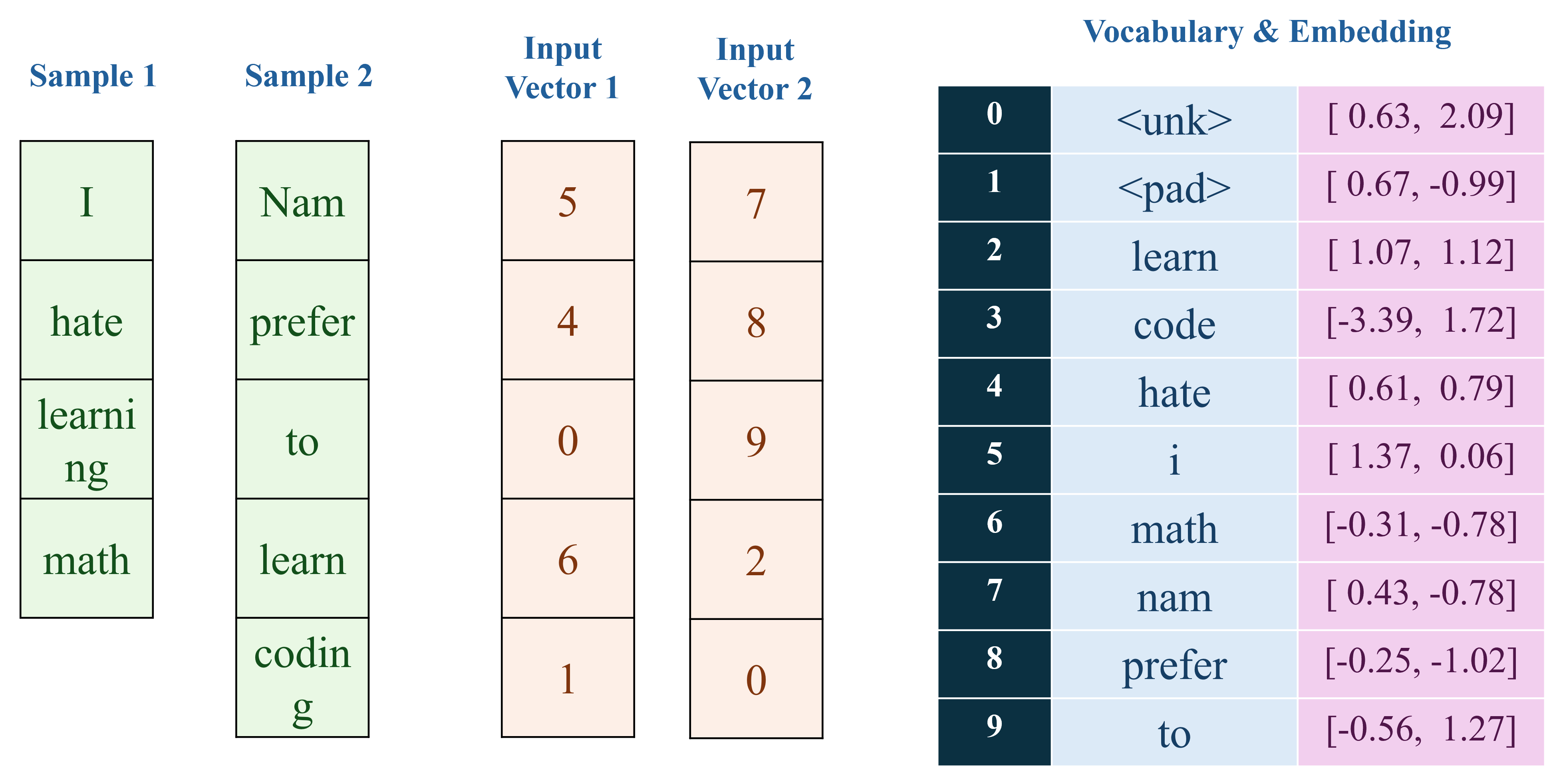
Trong các câu hỏi của phần text classification, POS tagging, chúng ta được cung cấp một tập dữ liệu nhỏ bao gồm hai chuỗi văn bản và các nhãn tương ứng trong đoạn code Python sau:
corpus = [ "I hate learning math", "Nam prefer to learn coding" ]
Quá trình tiền xử lý dữ liệu, xây dựng vocabulary, embedding được trực quan hóa như hình sau:
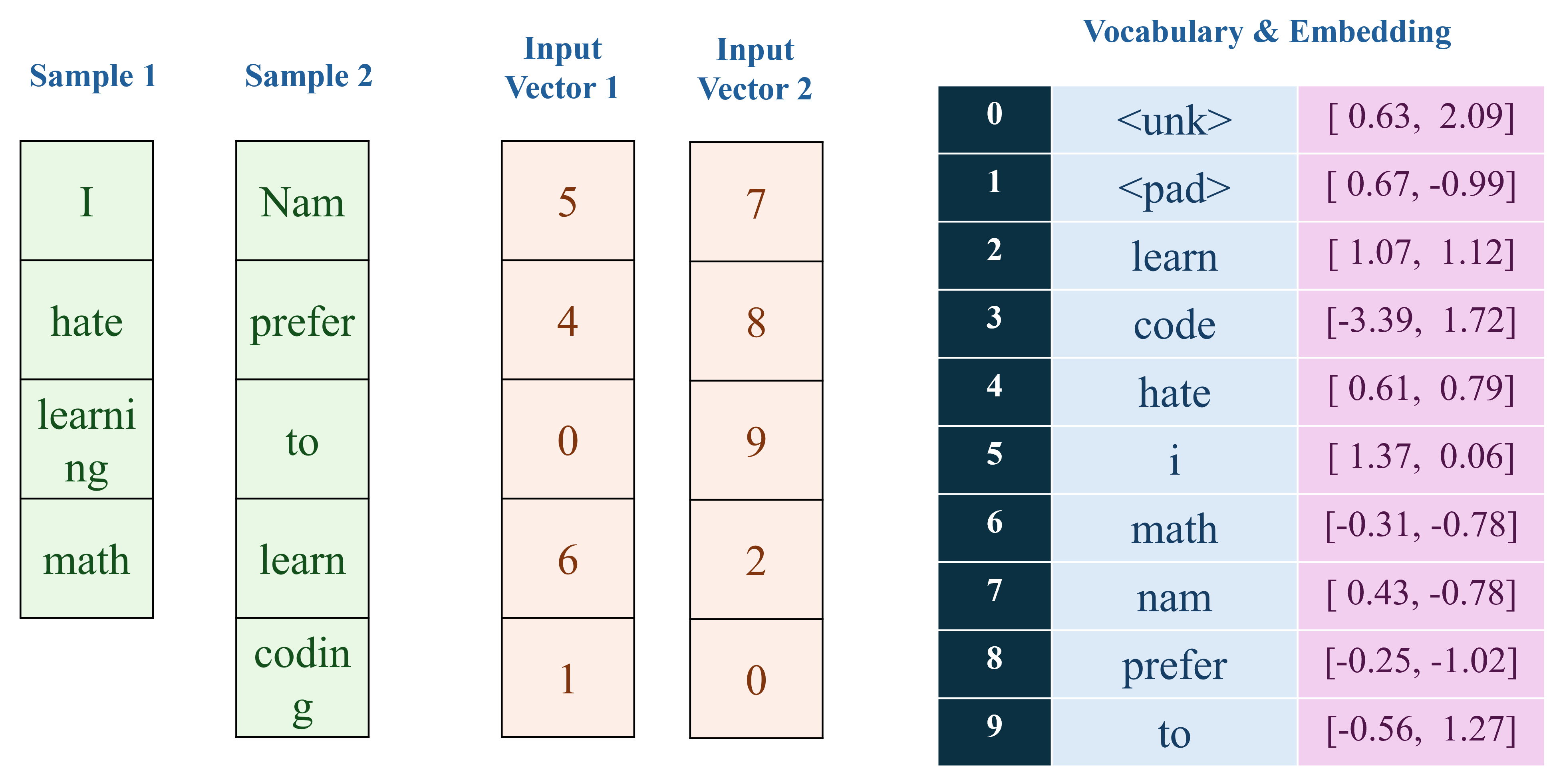
Mục tiêu của bài toán này là xây dựng một mô hình phần loại text (0-Negative, 1-Positive) với Baseline cụ thể như hình sau:
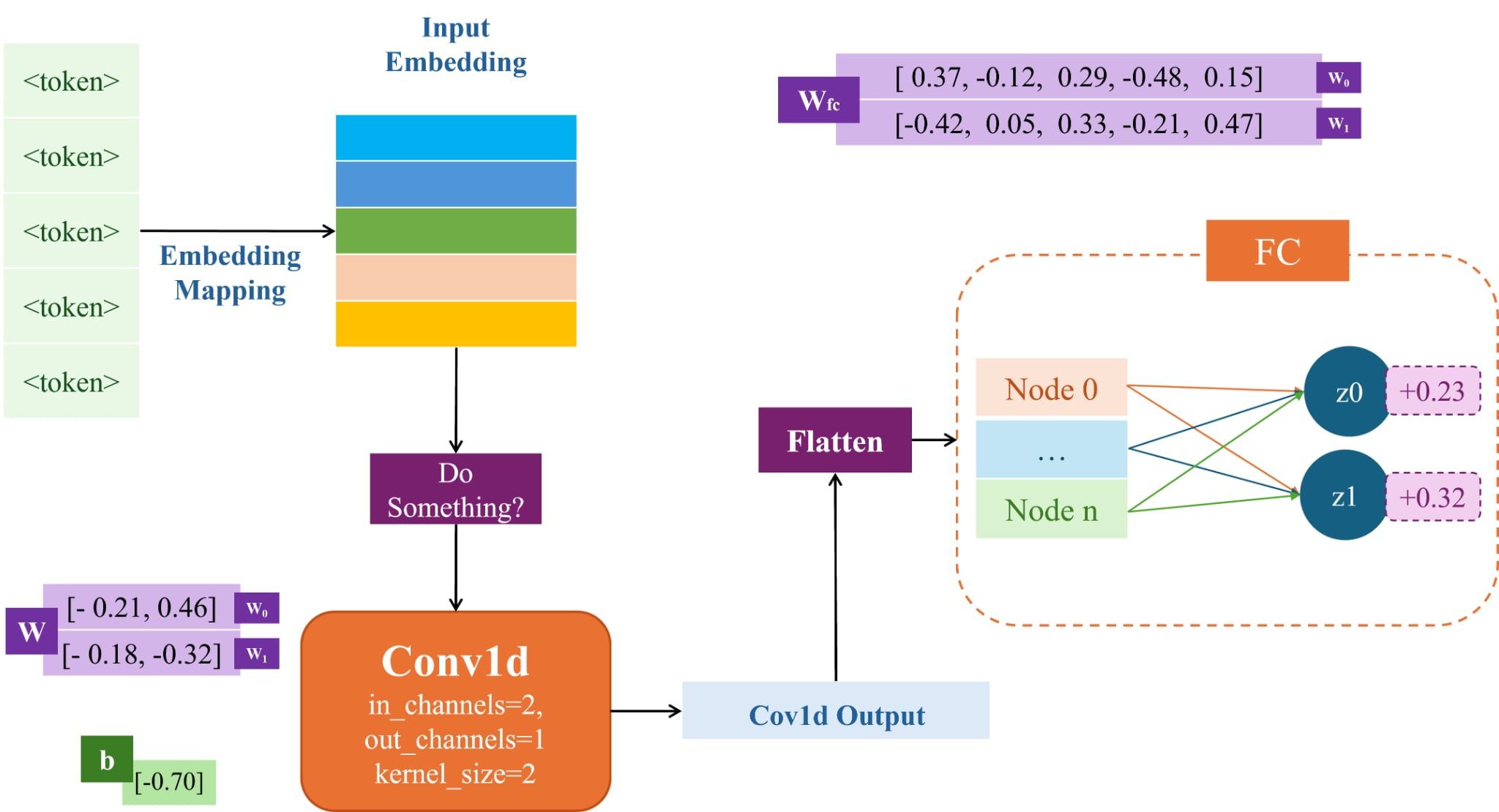
Dựa vào các thông tin có ở trong phần mô tả và hình vẽ, hãy đọc hiểu và trả lời câu hỏi sau:
import torch import torch.nn as nn from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator import nltk from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer corpus = [ "I hate learning math", "Nam prefer to learn coding" ] data_size = len(corpus) # 0: negative - 1: positive labels = [0, 1] # Define the max vocabulary size and sequence length vocab_size = 10 sequence_length = 5 nltk.download('punkt') stemmer = PorterStemmer() # Define tokenizer function tokenizer = get_tokenizer('basic_english') def tokenize(text): tokens = tokenizer(text) stemmed_tokens = [stemmer.stem(token) for token in tokens] return stemmed_tokens # Create a function to yield list of tokens def yield_tokens(examples): for text in examples: yield tokenize(text) # Create vocabulary vocab = build_vocab_from_iterator(yield_tokens(corpus), max_tokens=vocab_size, specials=["<unk>", "<pad>"]) vocab.set_default_index(vocab["<unk>"]) # Tokenize and numericalize your samples def vectorize(text, vocab, sequence_length): tokens = tokenizer(text) token_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokens][:sequence_length] token_ids = token_ids + [vocab["<pad>"]] * (sequence_length - len(tokens)) return torch.tensor(token_ids, dtype=torch.long) # Vectorize the samples corpus_ids = [] for sentence in corpus: corpus_ids.append(vectorize(sentence, vocab, sequence_length))
Hãy xác định shape đầu vào của convolution model Conv1d.
A. (1, 3, 6)
B. (1, 6, 3)
C. (1, 5, 2)
D. (1, 2, 5)
class TCls_Model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_classes): super().__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, 2) custem_weight = torch.tensor([ [ 0.63, 2.09], [ 0.67, -0.99], [ 1.07, 1.12], [-3.39, 1.72], [ 0.61, 0.79], [ 1.37, 0.06], [-0.31, -0.78], [ 0.43, -0.78], [-0.25, -1.02], [-0.56, 1.27] ]) self.embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(custem_weight) print((self.embedding.weight)) self.conv1d = nn.Conv1d(2, 1, kernel_size=2) custem_conv_weight = torch.tensor([ [[- 0.21, 0.46], [- 0.18, -0.32]] ]) self.conv1d.weight = nn.Parameter(custem_conv_weight) custem_conv_weight = torch.tensor( [-0.70] ) self.conv1d.bias = nn.Parameter(custem_conv_weight) print(self.conv1d.weight) print(self.conv1d.bias) self.fc = nn.Linear(5, num_classes) custom_fc_weight = torch.tensor([ [ 0.37, -0.12, 0.29, -0.48], [-0.42, 0.05, 0.33, -0.21] ]) self.fc.weight = nn.Parameter(custom_fc_weight) custem_fc_bias = torch.tensor( [0.23, 0.32] ) self.fc.bias = nn.Parameter(custem_fc_bias) print(self.fc.weight) print(self.fc.bias) self.flatten = nn.Flatten() def forward(self, x): x = self.embedding(x) print(x.shape) x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) print(x.shape) x = self.conv1d(x) print(x.shape) print(f"Output conv1d: {x}") x = self.flatten(x) print(x.shape) x = self.fc(x) print(f"result: {x}") return x num_classes = 2 model = TCls_Model(vocab_size, num_classes) input_1 = torch.tensor([[5, 4, 0, 6, 1]], dtype=torch.long) label_1 = torch.tensor([0], dtype=torch.long) output = model(input_1) print(output.shape)
torch.Size([1, 5, 2]) Shape đầu vào của Conv1: torch.Size([1, 2, 5]) torch.Size([1, 1, 4]) Output conv1d: tensor([[[-0.9707, -1.3493, -1.1015, 0.1305]]], grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 4]) result: tensor([[-0.3493, 0.2693]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 2])
Đáp án: D
Input của FC layer gồm bao nhiêu node?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Đáp án: B
Lớp "Conv1d" được định nghĩa với "kernel_size=2". Nó sẽ trượt một cửa sổ có kích thước 2 trên chuỗi đầu vào. Độ dài chuỗi đầu vào ("Length") là 5. Công thức tính độ dài chuỗi đầu ra là: . Áp dụng vào bài toán: .
Vậy, shape của tensor sau khi qua lớp "Conv1d" sẽ là "(1, 1, 4)" (Batch, Out Channels, New Length).
torch.Size([1, 1, 4])
Đâu là giá trị output của conv1d khi đưa sample1 vào model?
A. [ 0.25, -0.88, -0.73, 1.45]
B. [-1.01, -1.40, -1.20, 0.05]
C. [-0.97, -1.35, -1.10, 0.13]
D. [-0.12, 0.34, 0.55, -1.80]
torch.Size([1, 5, 2]) torch.Size([1, 2, 5]) torch.Size([1, 1, 4]) Output của conv1d: tensor([[[-0.9707, -1.3493, -1.1015, 0.1305]]], grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 4]) result: tensor([[-0.3493, 0.2693]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 2])
Đáp án: C
Biết rằng giá trị của vector output conv1d khi model nhận sample 2 là [-0.44, -1.13, -0.68, -1.51], hãy cho biết output của FC layer là bao nhiêu?
A. [0.73, 0.54]
B. [0.12, -0.89]
C. [-0.45, 1.02]
D. [0.00, 0.00]
torch.Size([1, 5, 2]) torch.Size([1, 2, 5]) torch.Size([1, 1, 4]) tensor([[[-0.4385, -1.1279, -0.6772, -1.5053]]], grad_fn=<ConvolutionBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 4]) Output của Conv1d: tensor([[0.7293, 0.5404]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>) torch.Size([1, 2])
Đáp án: A
Trong các câu hỏi của phần text classification, POS tagging, chúng ta được cung cấp một tập dữ liệu nhỏ bao gồm hai chuỗi văn bản và các nhãn tương ứng trong đoạn code Python sau:
corpus = [ "I hate learning math", "Nam prefer to learn coding" ]
Quá trình tiền xử lý dữ liệu, xây dựng vocabulary, embedding được trực quan hóa như hình sau:
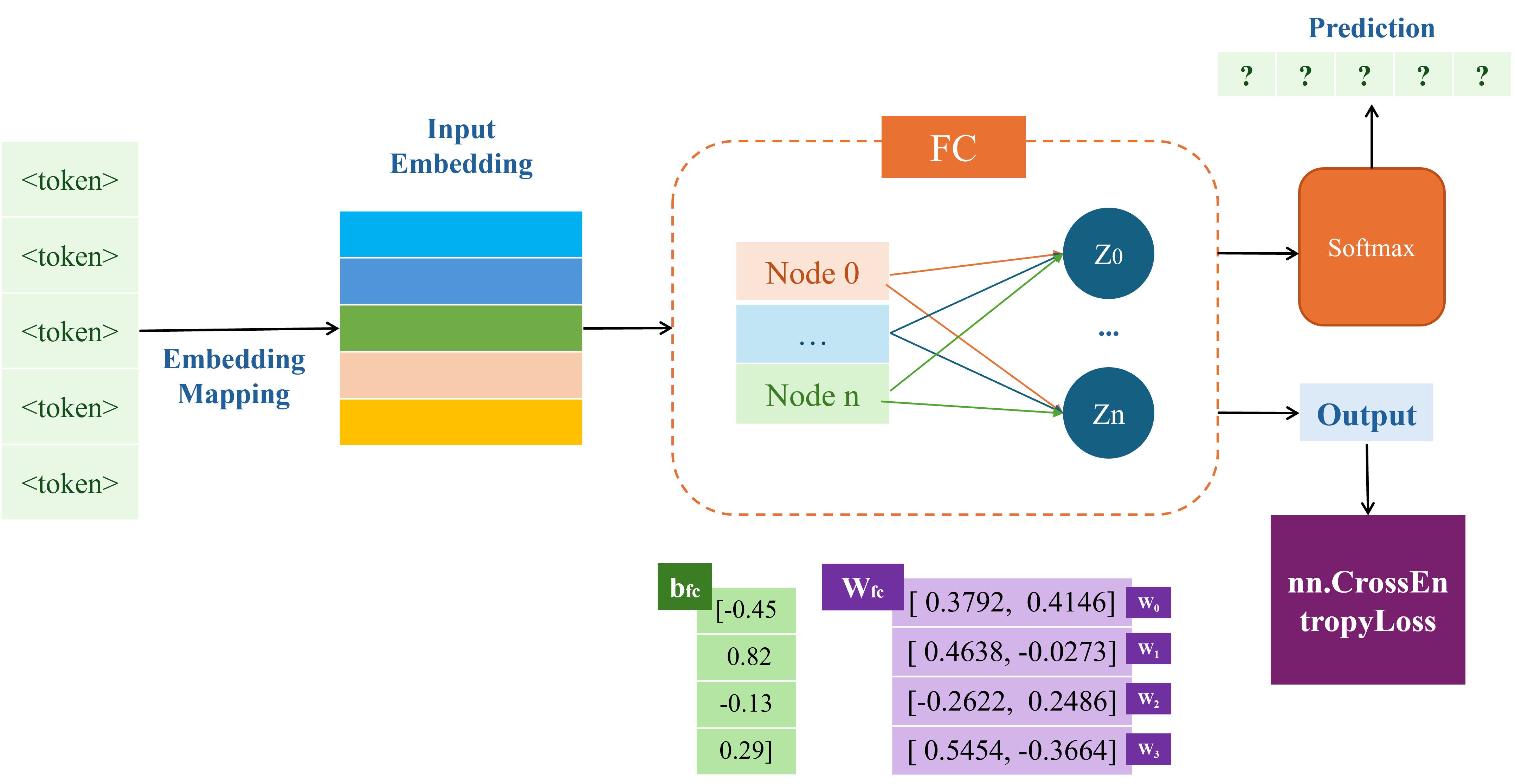
Mục tiêu của bài toán này là xây dựng một mô hình Part-of-speech Tagging (gồm 4 class: 0: noun/pronoun - 1: verb - others - 2, padding - 3) với Baseline cụ thể như hình sau:
import torch import torch.nn as nn from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator import nltk from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer corpus = [ "I hate learning math", "Nam prefer to learn coding" ] data_size = len(corpus) # 0: negative - 1: positive labels = [0, 1] # Define the max vocabulary size and sequence length vocab_size = 10 sequence_length = 5 nltk.download('punkt') stemmer = PorterStemmer() # Define tokenizer function tokenizer = get_tokenizer('basic_english') def tokenize(text): tokens = tokenizer(text) stemmed_tokens = [stemmer.stem(token) for token in tokens] return stemmed_tokens # Create a function to yield list of tokens def yield_tokens(examples): for text in examples: yield tokenize(text) # Create vocabulary vocab = build_vocab_from_iterator(yield_tokens(corpus), max_tokens=vocab_size, specials=["<unk>", "<pad>"]) vocab.set_default_index(vocab["<unk>"]) # Tokenize and numericalize your samples def vectorize(text, vocab, sequence_length): tokens = tokenizer(text) token_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokens][:sequence_length] token_ids = token_ids + [vocab["<pad>"]] * (sequence_length - len(tokens)) return torch.tensor(token_ids, dtype=torch.long) # Vectorize the samples corpus_ids = [] for sentence in corpus: corpus_ids.append(vectorize(sentence, vocab, sequence_length))
Output ở trong hình baseline (hay input của nn.CrossEntropyLoss) phải có shape bằng bao nhiêu?
A. (1, 2, 5)
B. (1, 5, 2)
C. (1, 4, 5)
D. (1, 5, 4)
class POS_Model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_classes): super().__init__() # Custom embedding layer self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, 2) custom_embedding_weight = torch.tensor([ [ 0.63, 2.09], [ 0.67, -0.99], [ 1.07, 1.12], [-3.39, 1.72], [ 0.61, 0.79], [ 1.37, 0.06], [-0.31, -0.78], [ 0.43, -0.78], [-0.25, -1.02], [-0.56, 1.27] ]) self.embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(custom_embedding_weight) print("Embedding weights:") print(self.embedding.weight) # Custom fully connected layer self.fc = nn.Linear(2, num_classes) custom_fc_weight = torch.tensor([ [0.3792, -0.4146], [0.4638, -0.0273], [-0.2622, 0.2486], [0.5454, -0.3664] ]) self.fc.weight = nn.Parameter(custom_fc_weight) custom_fc_bias = torch.tensor([-0.45, 0.82, -0.13, 0.29]) self.fc.bias = nn.Parameter(custom_fc_bias) print("FC weights:") print(self.fc.weight) print("FC bias:") print(self.fc.bias) def forward(self, x): print(f"Input shape: {x.shape}") x = self.embedding(x) print(f"After embedding shape: {x.shape}") x = self.fc(x) print(f"After FC shape: {x.shape}") print(x) x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) print(f"After permute shape: {x.shape}") return x model = POS_Model(vocab_size, 4) input_1 = torch.tensor([[5, 4, 0, 6, 1]], dtype=torch.long) label_1 = label_vecs[0] output = model(input_1)
Input shape: torch.Size([1, 5]) After embedding shape: torch.Size([1, 5, 2]) After FC shape: torch.Size([1, 5, 4]) tensor([[[ 0.0446, 1.4538, -0.4743, 1.0152], [-0.5462, 1.0814, -0.0935, 0.3332], [-1.0776, 1.0551, 0.2244, -0.1322], [-0.2442, 0.6975, -0.2426, 0.4067], [ 0.2145, 1.1578, -0.5518, 1.0182]]], grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>) After permute shape: torch.Size([1, 4, 5])
Đáp án: C
Hãy cho biết sau khi đưa sample 1 vào model, tính toán forward, đưa vào softmax, vector dự đoán của mô hình sẽ là?
A. [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
B. [3, 2, 1, 3, 1]
C. [2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
D. [3, 3, 3, 3, 3]
def softmax(x): return torch.softmax(x, dim=1) # Tính softmax softmax_out = softmax(output) print(torch.argmax(softmax_out, dim=1))
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
Đáp án: A
Trong các câu hỏi của phần Name Entity Recognition chúng ta được cung cấp một tập dữ liệu nhỏ bao gồm hai chuỗi văn bản và các nhãn tương ứng trong đoạn code Python sau:
corpus = [ "Tim Cook leads Apple in Cupertino", "Sam Altman is the CEO of OpenAI" ]
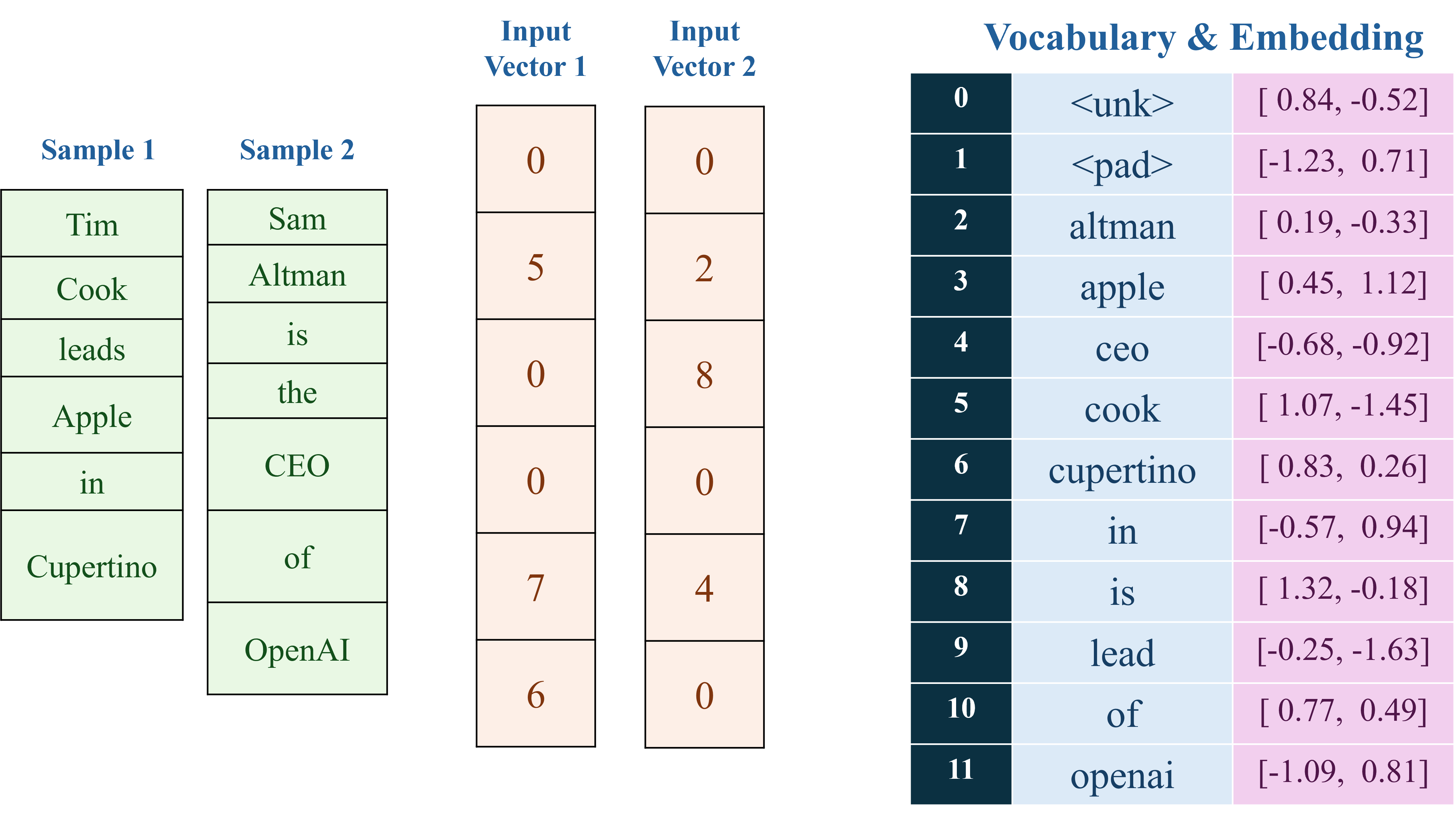
Mục tiêu của bài toán này là xây dựng một mô hình Name Entity Recognition, gồm 4 class: 0: B-Person 1: I-Person 2: B-Organization/Location 3: O 4: <pad> - padding
labels = [ [0, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2], [0, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2] ]
với Baseline cụ thể như hình sau:
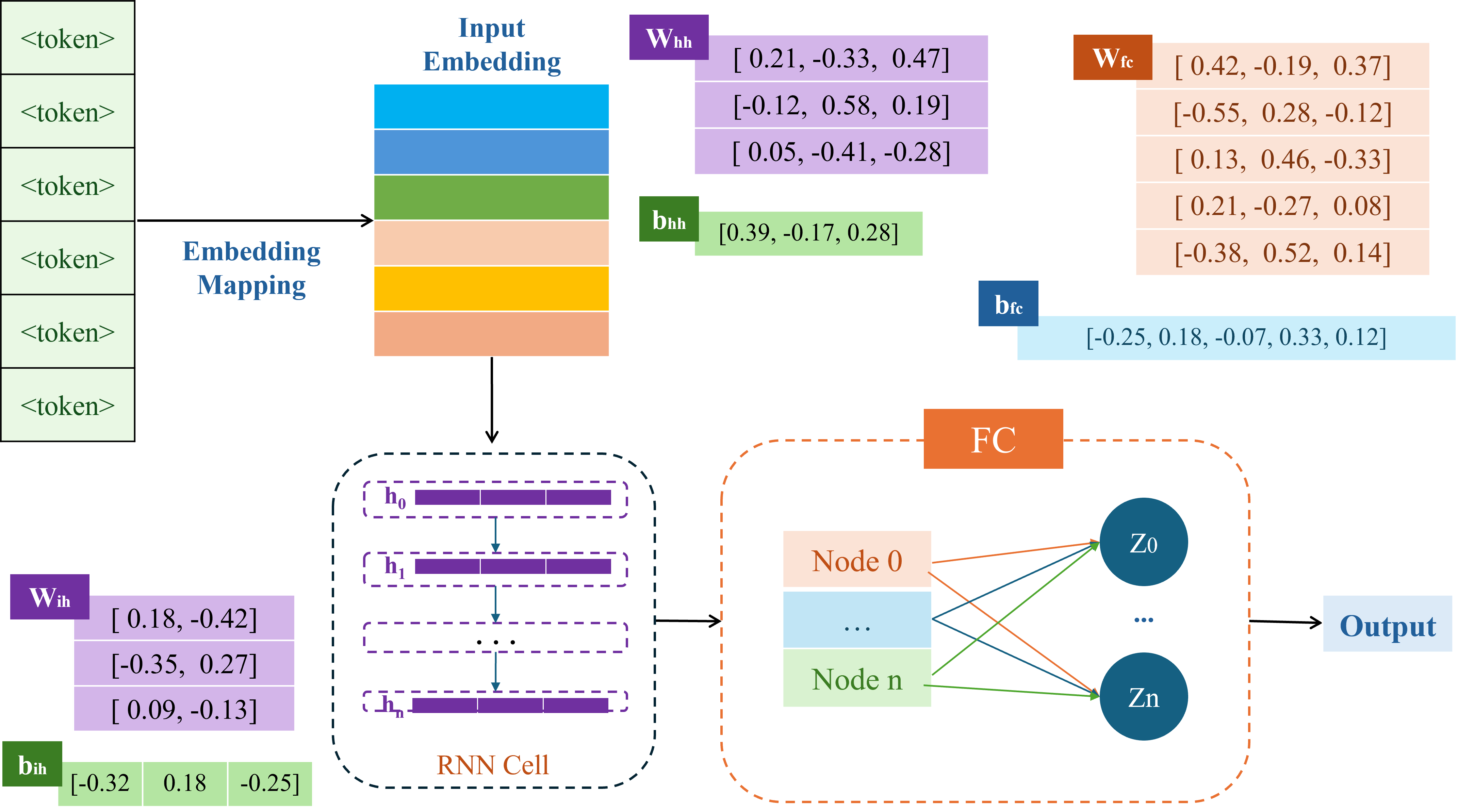
import torch import torch.nn as nn from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator import nltk from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer corpus = [ "Tim Cook leads Apple in Cupertino", "Sam Altman is the CEO of OpenAI" ] data_size = len(corpus) # Labeling scheme: # 0: B-Person, 1: I-Person # 2: B-Organization/Location, # 3: O (other) labels = [ [0, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2], [0, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2] ] # Define the max vocabulary size and sequence length vocab_size = 12 sequence_length = 6 num_classes = 4 + 1 # 4 classes + 1 for padding nltk.download('punkt') stemmer = PorterStemmer() # Define tokenizer function tokenizer = get_tokenizer('basic_english') def tokenize(text): tokens = tokenizer(text) stemmed_tokens = [stemmer.stem(token) for token in tokens] return stemmed_tokens # Create a function to yield list of tokens def yield_tokens(examples): for text in examples: yield tokenize(text) # Create vocabulary vocab = build_vocab_from_iterator(yield_tokens(corpus), max_tokens=vocab_size, specials=["<unk>", "<pad>"]) vocab.set_default_index(vocab["<unk>"]) # Tokenize and numericalize your samples def vectorize(text, vocab, sequence_length, sequence_label): tokens = tokenizer(text) token_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokens][:sequence_length] token_ids = token_ids + [vocab["<pad>"]] * (sequence_length - len(tokens)) sequence_label = sequence_label + [5] * (sequence_length - len(tokens)) sequence_label = sequence_label[:sequence_length] return torch.tensor(token_ids, dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor(sequence_label, dtype=torch.long) # Vectorize the samples sentence_vecs = [] label_vecs = [] for sentence, labels in zip(corpus, labels): sentence_vec, labels_vec = vectorize(sentence, vocab, sequence_length, labels) sentence_vecs.append(sentence_vec) label_vecs.append(labels_vec)
Output shape của FC layer là?
A. (1, 6, 5)
B. (1, 5, 6)
C. (1, 6, 6)
D. (1, 1, 6)
class NER_Model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_classes): super().__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, 2) custom_embedding_weight = torch.tensor([ [ 0.84, -0.52], [-1.23, 0.71], [ 0.19, -0.33], [ 0.45, 1.12], [-0.68, -0.92], [ 1.07, -1.45], [ 0.83, 0.26], [-0.57, 0.94], [ 1.32, -0.18], [-0.25, -1.63], [ 0.77, 0.49], [-1.09, 0.81] ]) self.embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(custom_embedding_weight) print("Embedding weights:") print(self.embedding.weight) # Custom RNN layer self.recurrent = nn.RNN(2, 3, batch_first=True) # Input-to-hidden weights (3x2) custom_rnn_weight_ih = torch.tensor([ [ 0.18, -0.42], [-0.35, 0.27], [ 0.09, -0.13] ]) # Hidden-to-hidden weights (3x3) custom_rnn_weight_hh = torch.tensor([ [ 0.21, -0.33, 0.47], [-0.12, 0.58, 0.19], [ 0.05, -0.41, -0.28] ]) # Input-to-hidden biases (3,) custom_rnn_bias_ih = torch.tensor([-0.32, 0.18, -0.25]) # Hidden-to-hidden biases (3,) custom_rnn_bias_hh = torch.tensor([0.39, -0.17, 0.28]) self.recurrent.weight_ih_l0 = nn.Parameter(custom_rnn_weight_ih) self.recurrent.weight_hh_l0 = nn.Parameter(custom_rnn_weight_hh) self.recurrent.bias_ih_l0 = nn.Parameter(custom_rnn_bias_ih) self.recurrent.bias_hh_l0 = nn.Parameter(custom_rnn_bias_hh) print("RNN weights and biases:") print(self.recurrent.weight_ih_l0) print(self.recurrent.weight_hh_l0) print(self.recurrent.bias_ih_l0) print(self.recurrent.bias_hh_l0) # Custom fully connected layer self.fc = nn.Linear(3, num_classes) custom_fc_weight = torch.tensor([ [ 0.42, -0.19, 0.37], [-0.55, 0.28, -0.12], [ 0.13, 0.46, -0.33], [ 0.21, -0.27, 0.08], [-0.38, 0.52, 0.14], ]) self.fc.weight = nn.Parameter(custom_fc_weight) custom_fc_bias = torch.tensor([[-0.25, 0.18, -0.07, 0.33, 0.12]]) self.fc.bias = nn.Parameter(custom_fc_bias) print("FC weights:") print(self.fc.weight) print("FC bias:") print(self.fc.bias) def forward(self, x): print(f"Input shape: {x.shape}") x = self.embedding(x) print(f"After embedding shape: {x.shape}") x, _ = self.recurrent(x) print(f"After RNN shape: {x.shape}") x = self.fc(x) print(f"After FC shape: {x.shape}") print(x) x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) print(f"After permute shape: {x.shape}") return x # create model model = NER_Model(vocab_size, num_classes) data = torch.tensor([[0, 5, 0, 0, 7, 6]]) output = model(data) print(output.shape)
Input shape: torch.Size([1, 6]) After embedding shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 2]) After RNN shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 3]) After FC shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 5]) tensor([[[ 0.0632, -0.1801, -0.2572, 0.5387, -0.2214], [ 0.3981, -0.5382, -0.4539, 0.7433, -0.5313], [ 0.3588, -0.4981, -0.4219, 0.7178, -0.4937], [ 0.3445, -0.4832, -0.4133, 0.7093, -0.4813], [-0.1715, 0.1055, -0.0584, 0.3546, 0.0980], [-0.1320, 0.0345, -0.1490, 0.4176, -0.0327]]], grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>) After permute shape: torch.Size([1, 5, 6]) torch.Size([1, 5, 6])
Đáp án: A
Hãy dùng token đầu tiên của sample 1 tính toán forward và trả về output cuối cùng. Dưới đây, đâu là kết quả tổng tất cả các phần tử trong vector output đó.
A. 0.2634
B. -0.4223
C. -0.0568
D. 0.0421
output = model(torch.tensor([[0]])) print(sum(output[0]))
tensor([-0.0568], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
Đáp án: C
Với phương pháp Extractive của bài toán Question Answering (QA), giai đoạn tiền xử lý dữ liệu của các bộ dữ liệu cho bài toán QA (ví dụ như: bộ SQuAD, Natural Questions, TyDi QA, ...) thường có các thuộc tính tương tự câu hỏi bên dưới, do đó cần nắm phải rõ cách xử lý chúng.
Cho một mẫu dữ liệu gồm 5 thuộc tính sau: Question, Context, Answer, Start, End. Trong đó:
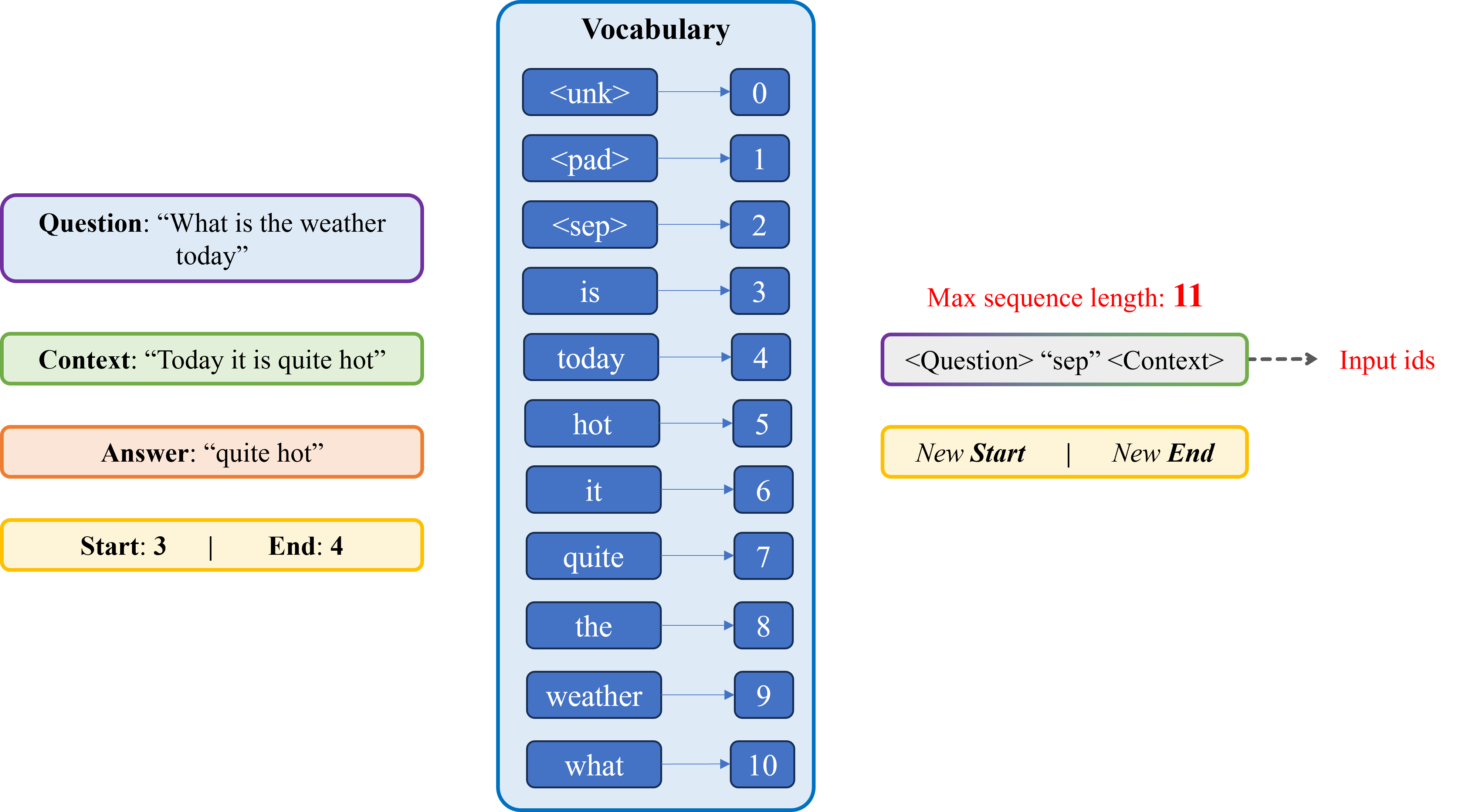
Cho trước bộ từ vựng (Vocabulary), hãy:
Chọn kết quả đúng trong các đáp án sau:
A. Input ids: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4, 2, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5], New Start: 9, New End: 10
B. Input ids: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5], New Start: 8, New End: 9
C. Input ids: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4, 2, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5], New Start: 9, New End: 11
D. Input ids: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5], New Start: 8, New End: 10\
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from collections import defaultdict from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator qa_dataset = [ { "context": "Today it is quite hot", "question": "What is the weather today", "answer": "quite hot", "start": 3, "end": 4 }, ] MAX_SEQ_LENGTH = 11 def vectorize(sample, vocab): input_text = sample["question"] + " <sep> " + sample["context"] print(f"Input Text: {input_text}") input_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokenizer(input_text)][:MAX_SEQ_LENGTH] print(f"Input Tokens: {input_ids} , Length: {len(input_ids)}") input_ids += [vocab["<pad>"]] * (MAX_SEQ_LENGTH - len(input_ids)) # Pad sequence print(f"Context Vector: {input_ids} , Length: {len(input_ids)}") answer_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokenizer(sample["answer"])] print(f"Answer Tokens: {answer_ids} , Length: {len(answer_ids)}") start_pos = input_ids.index(answer_ids[0]) end_pos = start_pos + len(answer_ids) - 1 print(f"New Start: {start_pos}, New End: {end_pos}") input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long) print(f"Input Vector: {input_ids}, Size: {input_ids.size()}") start_pos = torch.tensor(start_pos, dtype=torch.long) print(f"New Start: {start_pos}, Size: {start_pos.size()}") end_pos = torch.tensor(end_pos, dtype=torch.long) print(f"New End: {end_pos}, Size: {end_pos.size()}") return input_ids, start_pos, end_pos for sample in qa_dataset: sample["input_ids"], sample["start_token"], sample["end_token"] = vectorize(sample, vocab) print("-" * 50) def vectorize(sample, vocab): input_text = sample["question"] + " <sep> " + sample["context"] input_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokenizer(input_text)][:MAX_SEQ_LENGTH] input_ids += [vocab["<pad>"]] * (MAX_SEQ_LENGTH - len(input_ids)) answer_ids = [vocab[token] for token in tokenizer(sample["answer"])] start_pos = input_ids.index(answer_ids[0]) end_pos = start_pos + len(answer_ids) - 1 input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long) start_pos = torch.tensor(start_pos, dtype=torch.long) end_pos = torch.tensor(end_pos, dtype=torch.long) return input_ids, start_pos, end_pos class QADataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, dataset, vocab): self.dataset = dataset self.vocab = vocab def __len__(self): return len(self.dataset) def __getitem__(self, idx): return vectorize(self.dataset[idx], self.vocab) train_dataset = QADataset(qa_dataset, vocab) train_loader = DataLoader( train_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True ) for sample in train_loader: ids = sample[0].squeeze().tolist() detoken = ' '.join([vocab.get_itos()[id] for id in ids]) print(detoken) print(sample)
what is the weather today <sep> today it is quite hot [tensor([[10, 3, 8, 9, 4, 2, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5]]), tensor([9]), tensor([10])]
Đáp án: A
Trong bài này, Ta sẽ thực hiện tính toán quá trình inference của mô hình dịch máy dùng kiến trúc Encoder-Decoder như hình trên để dịch một câu từ tiếng Anh sang tiếng Việt. Bạn được cung cấp các thông tin sau:
Vocab của tiếng Anh và tiếng Việt với các token, index và embedding tương ứng:
Tiếng Anh:
| Token | Index | Embedding |
|---|---|---|
| <eos> | 0 | [ 1.1, -1.0] |
| I | 1 | [-1.5, 0.6] |
| hate | 2 | [-0.8, -1.3] |
| you | 3 | [ 0.3, 1.1] |
Tiếng Việt:
| Token | Index | Embedding |
|---|---|---|
| <sos> | 0 | [ -2.3, -0.3] |
| <eos> | 1 | [ 0.0, 0.0] |
| tôi | 2 | [ -0.2, -2.4] |
| ghét | 3 | [ 0.1, 2.1] |
| bạn | 4 | [ 0.1, 0.0] |
| em | 5 | [ -0.0, 0.2] |
| anh | 6 | [ -0.1, -0.2] |
Encoder: Nhận chuỗi các token tiếng Anh, đưa qua Embedding và sau đó qua RNN để tính toán hidden state tại mỗi bước.
Decoder:
Dựa trên các trọng số đã cung cấp, dưới đây là bảng cập nhật với các giá trị chính xác, đã được làm tròn đến một chữ số thập phân:
| Thành phần & Tham số | Giá trị |
|---|---|
| Trọng số Encoder RNN: Input-Hidden | [ -0.1, 1.1 ], [ 0.2, -1.1 ] |
| Bias Encoder RNN: Input-Hidden | [ -0.5, 0.7] |
| Trọng số Encoder RNN: Hidden-Hidden | [ -0.2, 1.1 ], [ 0.6, -0.2 ] |
| Bias Encoder RNN: Hidden-Hidden | [ 0.3, -0.0 ] |
| Trọng số Decoder RNN: Input-Hidden | [ 0.7, -1.3 ], [ -0.9, -0.8 ] |
| Bias Decoder RNN: Input-Hidden | [ 0.0, -0.9 ] |
| Trọng số Decoder RNN: Hidden-Hidden | [ -0.0, -0.1 ], [ -0.3, 1.4 ] |
| Bias Decoder RNN: Hidden-Hidden | [ -0.3, -0.7 ] |
| Trọng số Decoder FC Layer | [ 0.6, 0.3 ], [ -0.4, -0.8 ], [ -1.0, 1.7 ], [ 1.8, 1.7 ], [ 0.9, 0.2 ], [ 0.8, 0.3 ], [ -1.8, -0.4 ] |
| Bias Decoder FC Layer | [ -0.3, 0.4, 0.8, 0.7, -1.0, -1.2, 0.1 ] |
Với đầu vào là câu tiếng Anh "I hate you", bạn cần tính quá trình inference của mô hình để trả lời các câu hỏi.
Lưu ý: RNN áp dụng tanh cho các trạng thái ẩn.
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import torch.nn.functional as F ### Set seed for reproducibility torch.manual_seed(0) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False # ----------------------- # 1. TIỀN XỬ LÝ DỮ LIỆU # ----------------------- # Định nghĩa các token đặc biệt SOS_TOKEN = '<SOS>' EOS_TOKEN = '<EOS>' # Corpus cho tiếng Anh và tiếng Việt (chỉ một cặp câu) corpus_en = ["I hate you"] corpus_vi = ["tôi ghét bạn", "em ghét anh"] # Hàm tokenize: chuyển câu thành danh sách từ (chuyển về chữ thường) def tokenize(sentence): return sentence.lower().split() # Hàm xây dựng vocabulary: tạo từ điển cho các câu def build_vocab(sentences): tokens = [token for sentence in sentences for token in tokenize(sentence)] if 'i' in tokens: vocab = {EOS_TOKEN: 0} else: vocab = {SOS_TOKEN: 0, EOS_TOKEN: 1} idx = len(vocab) for token in tokens: if token not in vocab: vocab[token] = idx idx += 1 return vocab vocab_en = build_vocab(corpus_en) vocab_vi = build_vocab(corpus_vi) print("Từ điển tiếng Anh:", vocab_en) print("Từ điển tiếng Việt:", vocab_vi) # Chuyển corpus thành dữ liệu dạng indices data = [] for en, vi in zip(corpus_en, corpus_vi): src_indices = [vocab_en[token] for token in tokenize(en)] + [vocab_en[EOS_TOKEN]] trg_indices = [vocab_vi[SOS_TOKEN]] + [vocab_vi['tôi'], vocab_vi['ghét'], vocab_vi['anh']] + [vocab_vi[EOS_TOKEN]] data.append((src_indices, trg_indices)) print("Dữ liệu sau khi chuyển thành indices:", data)
# ----------------------- # 2. XÂY DỰNG CÁC LỚP MÔ HÌNH # ----------------------- # Các tham số hyper-parameter embedding_dim = 2 # Kích thước vector embedding (nhỏ để dễ tính tay) hidden_size = 2 # Kích thước hidden state của RNN # --- Encoder --- class Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, embedding_dim, hidden_size): super(Encoder, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_dim) self.rnn = nn.RNN(embedding_dim, hidden_size, batch_first=True) def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len) embedded = self.embedding(x) # (batch_size, seq_len, embedding_dim) # Khởi tạo hidden state hidden = torch.zeros(1, x.size(0), self.rnn.hidden_size).to(x.device) # (1, batch_size, hidden_size) outputs = [] for t in range(x.size(1)): # seq_len input_t = embedded[:, t, :].unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1, embedding_dim) output_t, hidden = self.rnn(input_t, hidden) outputs.append(output_t.squeeze(1)) outputs = torch.stack(outputs, dim=1) # (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size) return embedded, outputs, hidden # --- Decoder --- class Decoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, output_size, embedding_dim, hidden_size): super(Decoder, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, embedding_dim) self.rnn = nn.RNN(embedding_dim, hidden_size, batch_first=True) self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) def forward(self, x, hidden): # x: (batch_size, 1) -> token hiện tại embedded = self.embedding(x) # (batch_size, 1, embedding_dim) outputs, hidden = self.rnn(embedded, hidden) # outputs: (batch_size, 1, hidden_size) predictions = self.fc(outputs) # (batch_size, 1, output_size) return embedded, outputs, predictions, hidden # --- Seq2Seq (gộp Encoder và Decoder) --- class Seq2Seq(nn.Module): def __init__(self, encoder, decoder): super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__() self.encoder = encoder self.decoder = decoder def forward(self, src, trg): # src: (batch_size, src_len), trg: (batch_size, trg_len) batch_size = src.size(0) trg_len = trg.size(1) output_size = self.decoder.fc.out_features outputs = torch.zeros(batch_size, trg_len, output_size).to(src.device) # Encoder forward _, _, hidden = self.encoder(src) # Khởi tạo đầu vào cho decoder với token <SOS> input_token = trg[:, 0].unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1) for t in range(1, trg_len): _, dec_output, fc_output, hidden = self.decoder(input_token, hidden) outputs[:, t, :] = fc_output.squeeze(1) input_token = trg[:, t].unsqueeze(1) return outputs def manual_inference(self, src, max_len=10): # Inference theo từng bước, in ra các giá trị trung gian embedded, _, hidden = self.encoder(src) print("\n\n\n\n\n\n\n--------------------------------------------------------------") print("Câu 1:") print(hidden) print("Hidden state 1 của Encoder:", _[0][0].detach().numpy().round(4)) print("Hidden state 2 của Encoder:", _[0][1].detach().numpy().round(4)) print("--------------------------------------------------------------") print("\n\n\n\n\n\n\nEmbedding encoder:", embedded.detach().numpy().round(4)) input_token = torch.tensor([[vocab_vi[SOS_TOKEN]]]).to(src.device) print("Hidden state của Encoder:", hidden.squeeze(0).detach().numpy().round(4)) tokens_list = [] for t in range(max_len): emb, dec_output, fc_output, hidden = self.decoder(input_token, hidden) print(f"\n--- Decoder bước {t+1} ---") # In ra giá trị trung gian: current_token = list(vocab_vi.keys())[list(vocab_vi.values()).index(input_token.item())] print(f"Token đầu vào: '{current_token}'") print("Embedding của token:", emb.squeeze(0).detach().numpy().round(4)) print("Hidden state (output của RNN):", dec_output.squeeze(0).detach().numpy().round(4)) print("Đầu ra của FC (logits):", fc_output.squeeze(0).detach().numpy().round(4)) probs = F.softmax(fc_output.squeeze(0), dim=1) if t == 0 : print("\n\n\n\n--------------------------------------------------------------") print("Câu 2:") print("Xác suất (softmax):", probs.detach().numpy().round(4)) if t == 0 : print("--------------------------------------------------------------\n\n\n\n") top1 = fc_output.argmax(2) predicted_token = list(vocab_vi.keys())[list(vocab_vi.values()).index(top1.item())] print("Dự đoán token:", predicted_token) if top1.item() == vocab_vi[EOS_TOKEN]: break tokens_list.append(top1.item()) input_token = top1 return tokens_list
Biết chiều của hidden state là 2. Tính hidden state của encoder.
A. [ -0.9594 0.9819]
B. [-0.9574 0.9799]
C. [-0.9554 0.9779]
D. [ -0.9534 0.9759]
# Khởi tạo encoder, decoder và mô hình Seq2Seq encoder = Encoder(len(vocab_en), embedding_dim, hidden_size) decoder = Decoder(len(vocab_vi), embedding_dim, hidden_size) model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder) # ----------------------- # 3. HUẤN LUYỆN MÔ HÌNH # ----------------------- num_epochs = 140 learning_rate = 0.01 weight_decay = 0.0001 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay) # Huấn luyện trên corpus (chỉ 1 cặp câu) for epoch in range(num_epochs): total_loss = 0 for src_indices, trg_indices in data: src_tensor = torch.tensor(src_indices).unsqueeze(0) # (1, seq_len_src) trg_tensor = torch.tensor(trg_indices).unsqueeze(0) # (1, seq_len_trg) optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = model(src_tensor, trg_tensor) loss = 0 for t in range(1, trg_tensor.size(1)): loss += criterion(outputs[:, t, :], trg_tensor[:, t]) loss.backward() optimizer.step() total_loss += loss.item() if (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0: print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}, Loss: {total_loss / len(data)}") # ----------------------- # LÀM TRÒN TRỌNG SỐ TRƯỚC INFERENCE # ----------------------- def round_weights(model): with torch.no_grad(): for param in model.parameters(): param.copy_((param * 10).round() / 10) round_weights(model) # In ra trọng số của các layer – dữ liệu đề thi để thí sinh tính tay. print("\n--- Trọng số của các layer sau huấn luyện ---") print("Embedding Encoder:") print(model.encoder.embedding.weight.data) print("\nRNN weights Encoder (input-hidden):") print(model.encoder.rnn.weight_ih_l0.data) print("RNN bias Encoder (input-hidden):") print(model.encoder.rnn.bias_ih_l0.data) print("RNN weights Encoder (hidden-hidden):") print(model.encoder.rnn.weight_hh_l0.data) print("RNN bias Encoder (hidden-hidden):") print(model.encoder.rnn.bias_hh_l0.data) print("\nEmbedding Decoder:") print(model.decoder.embedding.weight.data) print("\nRNN weights Decoder (input-hidden):") print(model.decoder.rnn.weight_ih_l0.data) print("RNN bias Decoder (input-hidden):") print(model.decoder.rnn.bias_ih_l0.data) print("RNN weights Decoder (hidden-hidden):") print(model.decoder.rnn.weight_hh_l0.data) print("RNN bias Decoder (hidden-hidden):") print(model.decoder.rnn.bias_hh_l0.data) print("\nDecoder FC weights:") print(model.decoder.fc.weight.data) print("Decoder FC bias:") print(model.decoder.fc.bias.data) # ----------------------- # 4. HÀM INFERENCE VÀ TÍNH TAY (MANUAL INFERENCE) # ----------------------- test_sentence = "I hate you" src_indices = [vocab_en[token] for token in tokenize(test_sentence)] + [vocab_en[EOS_TOKEN]] src_tensor = torch.tensor(src_indices).unsqueeze(0) print("\n=== Inference tính tay cho câu: '{}' ===".format(test_sentence)) predicted_tokens = model.manual_inference(src_tensor) inv_vocab_vi = {idx: token for token, idx in vocab_vi.items()} translated_sentence = ' '.join([inv_vocab_vi[idx] for idx in predicted_tokens]) print("Câu dịch dự đoán: -->", translated_sentence)
-------------------------------------------------------------- Câu 1: tensor([[[-0.9874, 0.9923]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>) Hidden state 1 của Encoder: [ 0.5441 -0.2543] Hidden state 2 của Encoder: [-0.9594 0.9819] --------------------------------------------------------------
Đáp án: A
Biết hidden state cuối cùng của Encoder . Sau khi ở decoder được đưa qua lớp Fully Connected để tạo ra logits, áp dụng softmax lên logits, xác suất của token được chọn sẽ bằng bao nhiêu? Kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ 2.
A. 0.79
B. 0.63
C. 0.47
D. 0.31
-------------------------------------------------------------- Câu 2: --- Decoder bước 1 --- Token đầu vào: '<SOS>' Embedding của token: [[-2.3 -0.3]] Hidden state (output của RNN): [[-0.9245 0.9835]] Đầu ra của FC (logits): [[-0.5596 -0.017 3.3965 0.7079 -1.6354 -1.6446 1.3707]] Xác suất (softmax): [[0.0151 0.026 0.7906 0.0537 0.0052 0.0051 0.1043]] Dự đoán token: tôi --- Decoder bước 2 --- Token đầu vào: 'tôi' Embedding của token: [[-0.2 -2.4]] Hidden state (output của RNN): [[0.9886 0.9735]] Đầu ra của FC (logits): [[ 0.5852 -0.7742 1.4662 4.1344 0.0844 -0.1171 -2.0689]] Xác suất (softmax): [[0.0252 0.0065 0.0609 0.8778 0.0153 0.0125 0.0018]] Dự đoán token: ghét --- Decoder bước 3 --- Token đầu vào: 'ghét' Embedding của token: [[0.1 2.1]] Hidden state (output của RNN): [[-0.9956 -0.9802]] Đầu ra của FC (logits): [[-1.1914 1.5824 0.1292 -2.7585 -2.0921 -2.2905 2.2842]] Xác suất (softmax): [[0.0185 0.2965 0.0693 0.0039 0.0075 0.0062 0.5981]] Dự đoán token: anh --- Decoder bước 4 --- Token đầu vào: 'anh' Embedding của token: [[-0.1 -0.2]] Hidden state (output của RNN): [[-0.012 -0.9844]] Đầu ra của FC (logits): [[-0.6025 1.1923 -0.8615 -0.9951 -1.2077 -1.5049 0.5153]] Xác suất (softmax): [[0.0802 0.4824 0.0619 0.0541 0.0438 0.0325 0.2451]] Dự đoán token: <EOS> Câu dịch dự đoán: --> tôi ghét anh --------------------------------------------------------------
Đáp án: A
Trong bài này, Ta sẽ thực hiện tính toán quá trình inference của mô hình gen next token (gen text) dùng kiến trúc RNN như hình trên để tạo một câu từ một từ cho trước. Bạn được cung cấp các thông tin sau:
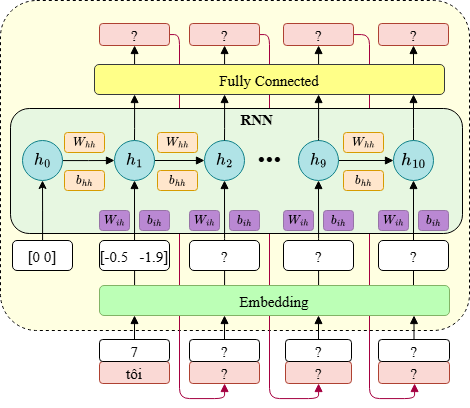
Vocab với các token, index và embedding tương ứng:
| Token | Index | Embedding |
|---|---|---|
| <eos> | 0 | [ -0.0, 0.1] |
| viên | 1 | [ -0.0, 0.0] |
| làm | 2 | [ 0.0, 0.0] |
| bá | 3 | [ 2.1, -0.4] |
| học | 4 | [ 0.2, 1.2] |
| sinh | 5 | [ 0.2, -0.0] |
| là | 6 | [ -1.1, 1.6] |
| tôi | 7 | [ -0.5, -1.9] |
| sư | 8 | [ 0.6, -0.1] |
| giáo | 9 | [ -0.0, 0.2] |
Dưới đây là bảng cập nhật với các trọng số sau khi huấn luyện:
| Thành phần & Tham số | Giá trị |
|---|---|
| Trọng số RNN: Input-Hidden | [ -1.1, 1.7 ], [ 1.4, 0.1 ] |
| Trọng số RNN: Hidden-Hidden | [ 0.4, -0.5 ], [ 1.7, -0.7 ] |
| Trọng số Decoder FC Layer | [ -1.8, 1.9 ], [ 0.2, -0.4 ], [ 0.4, -0.5 ], [ 1.4, 2.0 ], [ 2.0, -2.4 ], [ 0.4, -0.5 ], [ -1.9, -0.8 ], [ 0.4, -0.5 ], [ 0.4, -0.5 ], [ 0.4, -0.5 ] |
Với đầu vào là từ "tôi", bạn cần tính quá trình inference của mô hình để trả lời các câu hỏi.
Lưu ý: RNN áp dụng tanh cho các trạng thái ẩn.
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import numpy as np import random def set_random_seed(seed): torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) random.seed(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
Biết chiều hidden state = 2. Sau khi được đưa qua lớp Fully Connected để tạo ra logits, áp dụng softmax lên logits, xác suất của token được chọn sẽ bằng bao nhiêu? Kết quả cuối cùng được làm tròn đến chữ số thập phân thứ 2.
A. 0.70
B. 0.58
C. 0.46
D. 0.34
class SimpleRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_size): super(SimpleRNN, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim) self.rnn = nn.RNN(embedding_dim, hidden_size, batch_first=True, bias=False) self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size, bias=False) def forward(self, src, trg): batch_size = trg.size(0) trg_len = trg.size(1) output_size = self.fc.out_features outputs = torch.zeros(batch_size, trg_len, output_size).to(src.device) embedded = self.embedding(src) hidden = None for t in range(trg_len): input_embedded = embedded[:, t, :] rnn_out, hidden = self.rnn(input_embedded, hidden) prediction = self.fc(rnn_out) outputs[:, t, :] = prediction.squeeze(1) return outputs def manual_inference(self, start_word="tôi", max_len=10, vocab=None, idx_to_word=None): """ Manual inference starting with a specific word with detailed tensor calculations """ print(f"\n=== Chi tiết inference bắt đầu với '{start_word}' ===") self.eval() with torch.no_grad(): # Đảm bảo bắt đầu với từ cụ thể (mặc định "tôi") if start_word in vocab: start_token_idx = vocab[start_word] else: print(f"Warning: '{start_word}' not in vocabulary. Using default start.") start_token_idx = vocab.get("tôi", 1) # Default to first non-EOS token if "tôi" not found input_token = torch.tensor([start_token_idx]) current_token_idx = start_token_idx print(f"Token bắt đầu: {idx_to_word[current_token_idx]} (index: {current_token_idx})") # Initialize hidden state hidden = None # Store generated indices (start with the input token) generated_indices = [current_token_idx] # Generation loop for t in range(max_len): print(f"\n--- Bước {t+1}: Xử lý token '{idx_to_word[current_token_idx]}' ---") # Embed input token print(f"Input token tensor: {input_token}") embedded = self.embedding(input_token) print(f"Embedding tensor: {embedded}") # Reshape for RNN input embedded_reshaped = embedded.unsqueeze(1) print(f"Reshaped embedding tensor: {embedded_reshaped}") # Pass through RNN print("Passing through RNN...") rnn_out, hidden = self.rnn(embedded_reshaped, hidden) print(f"RNN output tensor: {rnn_out}") print(f"RNN hidden state tensor: {hidden}") # Get prediction through fully connected layer print("Passing through fully connected layer...") prediction = self.fc(rnn_out) print(f"Raw prediction tensor: {prediction}") # Get token probabilities token_probs = torch.softmax(prediction.squeeze(), dim=0) print(f"Token probabilities after softmax: {token_probs}") print(f"Sum of probabilities: {token_probs.sum().item()}") # Get top predictions top_probs, top_indices = torch.topk(token_probs, 3) print("\nTop 3 predictions:") for i in range(min(3, len(top_indices))): token_idx = top_indices[i].item() token_word = idx_to_word[token_idx] prob = top_probs[i].item() print(f" {token_word} (index: {token_idx}): {prob:.4f}") # Get most likely next token next_token = prediction.argmax(2).squeeze() next_token_idx = next_token.item() next_token_word = idx_to_word[next_token_idx] print(f"\nSelected next token: {next_token_word} (index: {next_token_idx})") # Stop if EOS if next_token_idx == vocab['<EOS>']: print("Reached EOS token, stopping generation") break # Add prediction to generated sequence generated_indices.append(next_token_idx) # Update input for next iteration input_token = torch.tensor([next_token_idx]) current_token_idx = next_token_idx # Convert indices to words and print full sentence generated_words = [idx_to_word[idx] for idx in generated_indices] generated_sentence = " ".join(generated_words) print("\n\n\n\n--------------------------------------------------------------") print("Câu 2:") print(f"\nCâu được tạo: {generated_sentence}") print("--------------------------------------------------------------") return generated_indices, generated_sentence
!gdown 1XiQofwvc3aQm_umVkdfasvhMi_Afm2OK
# Vocabulary (index to word mapping) vocab_vi = {'<EOS>': 0, 'viên': 1, 'làm': 2, 'bá': 3, 'học': 4, 'sinh': 5, 'là': 6, 'tôi': 7, 'sư': 8, 'giáo': 9} vocab_size = len(vocab_vi) embedding_dim = 2 hidden_size = 2 set_random_seed(10) model = SimpleRNN(vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_size) model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model.pth")) model.eval() # In trọng số sau khi huấn luyện print("\nTrọng số sau khi huấn luyện:") for name, param in model.named_parameters(): print(f"{name}: {param.shape}") print(param) model.manual_inference(start_word="tôi", max_len=10, vocab=vocab_vi, idx_to_word=idx_to_word)
=== Chi tiết inference bắt đầu với 'tôi' === Token bắt đầu: tôi (index: 7) --- Bước 1: Xử lý token 'tôi' --- Input token tensor: tensor([7]) Embedding tensor: tensor([[-0.5000, -1.9000]]) Reshaped embedding tensor: tensor([[[-0.5000, -1.9000]]]) Passing through RNN... RNN output tensor: tensor([[[-0.9906, -0.7114]]]) RNN hidden state tensor: tensor([[[-0.9906, -0.7114]]]) Passing through fully connected layer... Raw prediction tensor: tensor([[[ 0.4315, 0.0864, -0.0406, -2.8097, -0.2739, -0.0406, 2.4513, -0.0406, -0.0406, -0.0406]]]) Token probabilities after softmax: tensor([0.0775, 0.0549, 0.0484, 0.0030, 0.0383, 0.0484, 0.5844, 0.0484, 0.0484, 0.0484]) Sum of probabilities: 1.0 Top 3 predictions: là (index: 6): 0.5844 <EOS> (index: 0): 0.0775 viên (index: 1): 0.0549 Selected next token: là (index: 6)
Đáp án: B
Câu hỏi :
Hãy tính toán và cho biết câu được dự đoán bởi mô hình là gì?
A. "tôi là học sinh"
B. "tôi là giáo viên"
C. "tôi làm giáo viên"
D. "tôi là học bá"
--- Bước 1: Xử lý token 'tôi' --- Input token tensor: tensor([7]) Embedding tensor: tensor([[-0.5000, -1.9000]]) Reshaped embedding tensor: tensor([[[-0.5000, -1.9000]]]) Passing through RNN... RNN output tensor: tensor([[[-0.9906, -0.7114]]]) RNN hidden state tensor: tensor([[[-0.9906, -0.7114]]]) Passing through fully connected layer... Raw prediction tensor: tensor([[[ 0.4315, 0.0864, -0.0406, -2.8097, -0.2739, -0.0406, 2.4513, -0.0406, -0.0406, -0.0406]]]) Token probabilities after softmax: tensor([0.0775, 0.0549, 0.0484, 0.0030, 0.0383, 0.0484, 0.5844, 0.0484, 0.0484, 0.0484]) Sum of probabilities: 1.0 Top 3 predictions: là (index: 6): 0.5844 <EOS> (index: 0): 0.0775 viên (index: 1): 0.0549 Selected next token: là (index: 6) --- Bước 2: Xử lý token 'là' --- Input token tensor: tensor([6]) Embedding tensor: tensor([[-1.1000, 1.6000]]) Reshaped embedding tensor: tensor([[[-1.1000, 1.6000]]]) Passing through RNN... RNN output tensor: tensor([[[ 0.9992, -0.9883]]]) RNN hidden state tensor: tensor([[[ 0.9992, -0.9883]]]) Passing through fully connected layer... Raw prediction tensor: tensor([[[-3.6762, 0.5951, 0.8938, -0.5777, 4.3702, 0.8938, -1.1078, 0.8938, 0.8938, 0.8938]]]) Token probabilities after softmax: tensor([2.6933e-04, 1.9289e-02, 2.6002e-02, 5.9696e-03, 8.4095e-01, 2.6002e-02, 3.5134e-03, 2.6002e-02, 2.6002e-02, 2.6002e-02]) Sum of probabilities: 0.9999999403953552 Top 3 predictions: học (index: 4): 0.8409 sư (index: 8): 0.0260 tôi (index: 7): 0.0260 Selected next token: học (index: 4) --- Bước 3: Xử lý token 'học' --- Input token tensor: tensor([4]) Embedding tensor: tensor([[0.2000, 1.2000]]) Reshaped embedding tensor: tensor([[[0.2000, 1.2000]]]) Passing through RNN... RNN output tensor: tensor([[[0.9913, 0.9925]]]) RNN hidden state tensor: tensor([[[0.9913, 0.9925]]]) Passing through fully connected layer... Raw prediction tensor: tensor([[[ 0.1015, -0.1987, -0.0997, 3.3727, -0.3995, -0.0997, -2.6774, -0.0997, -0.0997, -0.0997]]]) Token probabilities after softmax: tensor([0.0304, 0.0226, 0.0249, 0.8022, 0.0185, 0.0249, 0.0019, 0.0249, 0.0249, 0.0249]) Sum of probabilities: 0.9999999403953552 Top 3 predictions: bá (index: 3): 0.8022 <EOS> (index: 0): 0.0304 tôi (index: 7): 0.0249 Selected next token: bá (index: 3) --- Bước 4: Xử lý token 'bá' --- Input token tensor: tensor([3]) Embedding tensor: tensor([[ 2.1000, -0.4000]]) Reshaped embedding tensor: tensor([[[ 2.1000, -0.4000]]]) Passing through RNN... RNN output tensor: tensor([[[-0.9959, 0.9992]]]) RNN hidden state tensor: tensor([[[-0.9959, 0.9992]]]) Passing through fully connected layer... Raw prediction tensor: tensor([[[ 3.6910, -0.5988, -0.8979, 0.6041, -4.3897, -0.8979, 1.0928, -0.8979, -0.8979, -0.8979]]]) Token probabilities after softmax: tensor([8.4396e-01, 1.1569e-02, 8.5780e-03, 3.8523e-02, 2.6117e-04, 8.5780e-03, 6.2799e-02, 8.5780e-03, 8.5780e-03, 8.5780e-03]) Sum of probabilities: 0.9999999403953552 Top 3 predictions: <EOS> (index: 0): 0.8440 là (index: 6): 0.0628 bá (index: 3): 0.0385 Selected next token: <EOS> (index: 0) Reached EOS token, stopping generation -------------------------------------------------------------- Câu 2: Câu được tạo: tôi là học bá --------------------------------------------------------------
Đáp án: D
Cho hình bên dưới, chúng ta có đầu vào là một ma trận 4x4 và một mạng U-Net phiên bản đơn giản với kiến trúc như sau:
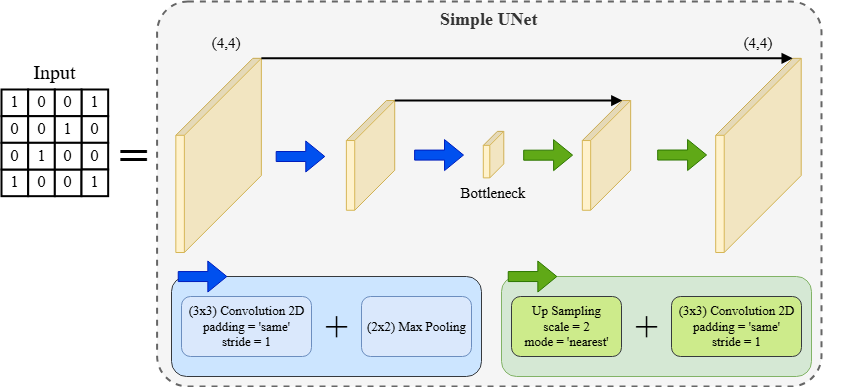
Encoder:
Gồm 2 bước down-sampling:
Conv1: kernel 3x3, padding='same', toàn bộ trọng số = 1, không dùng bias
Max Pooling: kernel 2x2, stride=2
Conv2: kernel 3x3, padding='same', toàn bộ trọng số = 1, không dùng bias
Max Pooling: kernel 2x2, stride=2
Kết quả cuối cùng của bước này là bottleneck.
Decoder:
Gồm 2 bước up-sampling:
Upsampling 1: scale=2, mode='nearest'
Conv3: kernel 3x3, padding='same', toàn bộ trọng số = 1, không dùng bias
Skip Connection 1: cộng với đầu ra của Conv2
Upsampling 2: scale=2, mode='nearest'
Conv4: kernel 3x3, padding='same', toàn bộ trọng số = 1, không dùng bias
Skip Connection 2: cộng với đầu ra của Conv1
Đầu ra cuối cùng (4x4) là output của Conv4.
Lưu ý: Các lớp convolution trong bài này đều dùng kernel 3x3 chứa toàn bộ trọng số bằng 1, không có bias, input và output đều có chiều sâu là 1
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import numpy as np import random def set_random_seed(seed): torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) random.seed(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False set_random_seed(0) class SimpleUNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(SimpleUNet, self).__init__() # Định nghĩa các lớp convolution với kernel 3x3, padding=1, không dùng bias. self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) # Các conv trong decoder sẽ được đặt sau upsampling self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False) # Khởi tạo trọng số cho các lớp convolution: tất cả bằng 1. for conv in [self.conv1, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4]: nn.init.constant_(conv.weight, 1) # Định nghĩa các lớp pooling và upsampling. self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest') def forward(self, x): outputs = {} # Encoder out_conv1 = self.conv1(x) # Kích thước: 4x4 outputs['conv1'] = out_conv1 # Skip connection từ conv1 out_pool1 = self.pool(out_conv1) # 4x4 -> 2x2 outputs['down1'] = out_pool1 out_conv2 = self.conv2(out_pool1) # 2x2 (giữ nguyên kích thước) outputs['conv2'] = out_conv2 # Skip connection từ conv2 bottleneck = self.pool(out_conv2) # 2x2 -> 1x1 outputs['bottleneck'] = bottleneck # Decoder # Bước 1: Upsample bottleneck, sau đó conv và mới skip với conv2 up1 = self.upsample(bottleneck) # 1x1 -> 2x2 outputs['up1'] = up1 conv_after_up1 = self.conv3(up1) # conv sau upsampling (2x2) outputs['conv_after_up1'] = conv_after_up1 merge1 = conv_after_up1 + out_conv2 # Skip connection từ conv2 outputs['merge1'] = merge1 # Bước 2: Upsample merge1, sau đó conv và mới skip với conv1 up2 = self.upsample(merge1) # 2x2 -> 4x4 outputs['up2'] = up2 conv_after_up2 = self.conv4(up2) # conv sau upsampling (4x4) outputs['conv_after_up2'] = conv_after_up2 merge2 = conv_after_up2 + out_conv1 # Skip connection từ conv1 outputs['merge2'] = merge2 # Output cuối cùng outputs['final'] = merge2 return outputs
Tính ma trận bottleneck sau khi thực hiện 2 lần down-sampling.
A. [[3]]
B. [[4]]
C. [[12]]
D. [[16]]
# Khởi tạo ma trận đầu vào 4x4 input_matrix = torch.tensor([[1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1]], dtype=torch.float32) # Chuyển về dạng tensor 4D: [batch_size, channes, height, width] input_tensor = input_matrix.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # Khởi tạo mô hình và chạy forward model = SimpleUNet() outputs = model(input_tensor) print("Input:") print(input_tensor.squeeze(0).squeeze(0)) # In ra kết quả của từng lớp và shape tương ứng for layer_name, output in outputs.items(): print(f"{layer_name}:") print(output.squeeze(0).squeeze(0)) print("-"*40)
bottleneck: tensor([[12.]], grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
Đáp án: C
Tính output cuối cùng của mạng.
A. [[241, 362, 362, 242], [362, 543, 543, 362], [362, 543, 543, 362], [242, 362, 362, 241]]
B. [[211, 332, 332, 212], [332, 513, 513, 332], [332, 513, 513, 332], [212, 332, 332, 211]]
C. [[181, 302, 302, 182], [302, 483, 483, 302], [302, 483, 483, 302], [182, 302, 302, 181]]
D. [[151, 272, 272, 152], [272, 453, 453, 272], [272, 453, 453, 272], [152, 272, 272, 151]]
final: tensor([[241., 362., 362., 242.], [362., 543., 543., 362.], [362., 543., 543., 362.], [242., 362., 362., 241.]], grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
Đáp án: A
Bài viết liên quan
Bài thi cuối khóa AIO2024 - Phần 1 (Machine Learning)
tháng 6 2025
Phần 1 trong bốn phần thi cuối khóa AIO2024. Phần này kiểm tra kiến thức machine learning với các kỹ năng và kiến thức về toán và lập trình Python.

Bài thi cuối khóa AIO2024 - Phần 2 (Deep Learning)
tháng 6 2025
Phần 2 trong bốn phần thi cuối khóa AIO2024. Phần này kiểm tra kiến thức deep learning với mô hình như CNN, RNN, LTSM và Transformer.
